Blue PVC Geomembrane
Cost-Effective Solution
Typically 10–20% cheaper than HDPE or EPDM alternatives with comparable performance, reducing project budgets.
Easy Weldability
Seamlessly fused via hot wedge or extrusion welding, creating airtight seams with minimal leakage risks.
High Puncture Resistance
Thick formulations (e.g., 1.5mm) withstand sharp objects, rocks, or debris in demanding environments like construction sites.
Blue PVC geomembranes are specialized containment materials engineered for applications requiring enhanced UV resistance, aesthetic appeal, and thermal stability. While sharing core properties with standard PVC liners, their distinctive coloration introduces unique advantages in environmental protection, aquaculture, and decorative infrastructure. This article explores the technical specifications, applications, and sustainability aspects of blue PVC geomembranes, supported by industry data and performance metrics.
Technical Specifications of Blue PVC Geomembranes
The coloration process for blue PVC geomembranes involves pigment integration during manufacturing, which slightly alters mechanical properties compared to standard black variants. Below is a detailed technical table comparing key specifications:
| Property | Specification Range | Testing Standard |
Thickness | 0.5mm – 3.0mm | ASTM D5199 |
Density | 1.45 – 1.55 g/cm³ | ASTM D792 |
Tensile Strength (MD/CD) | 18–28 MPa (MD), 16–24 MPa (CD) | ASTM D6693 |
Elongation at Break (MD/CD) | 250–350% (MD/CD) | ASTM D6693 |
Puncture Resistance | 150–250 N | ASTM D4833 |
Carbon Black Content | 0.5–1.0% (reduced vs. black PVC) | ASTM D1603 |
Pigment Type | Organic UV-stable dyes | Internal Lab Testing |
Light Reflectance | 30–40% (blue) vs. 5–10% (black) | ASTM E903 |
UV Resistance | 2,000+ hours (ASTM G154) | ASTM D4437 |
Operating Temperature Range | -25°C to +65°C | Internal Lab Testing |
Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, oils | ASTM D5322 |
Water Vapor Permeability | <0.1 g/cm²/day | ASTM E96 |
Key Differences From Standard PVC
Reduced Carbon Black: Blue pigments partially replace carbon black, slightly lowering UV resistance but improving aesthetic appeal.
Enhanced Light Reflectance: The blue hue reflects 30–40% of sunlight, reducing thermal expansion in exposed applications.
Pigment Stability: Specialized dyes resist fading, maintaining color vibrancy for 10+ years.
Applications of Blue PVC Geomembranes
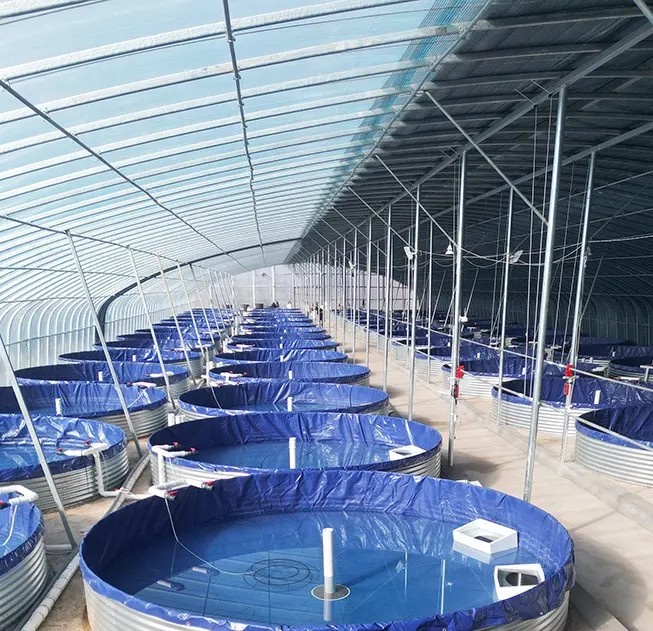
1. Aquaculture Ponds and Tanks
Use Case: Liners for ornamental fish farms, shrimp ponds, and aquaponics systems.
Advantages:
Blue color suppresses algae growth by limiting light penetration.
Non-toxic formulation ensures aquatic safety.
High flexibility accommodates pond shape variations.
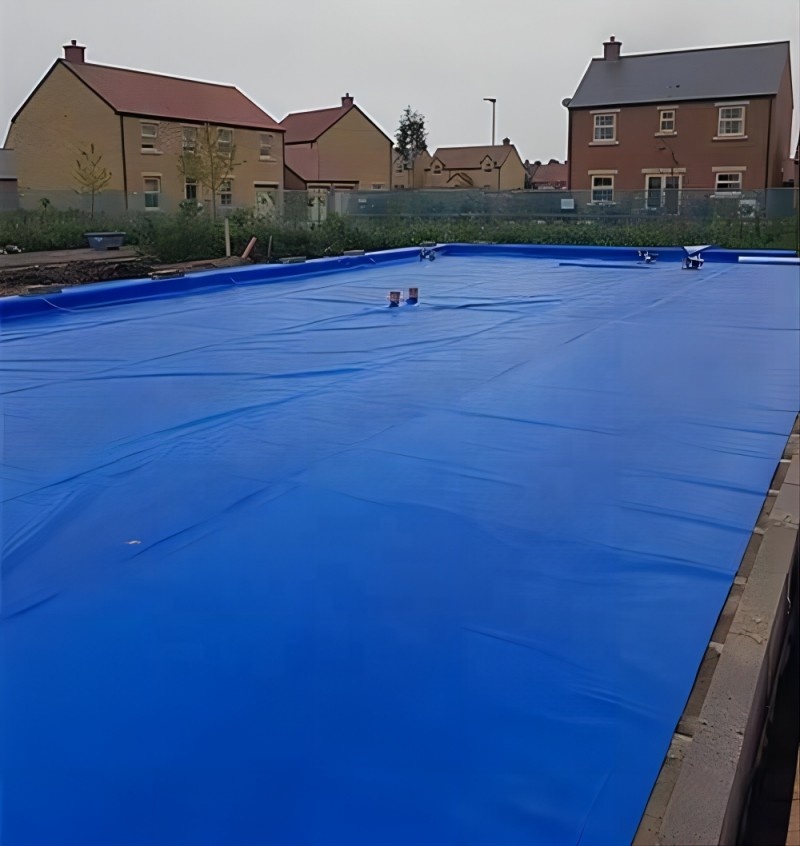
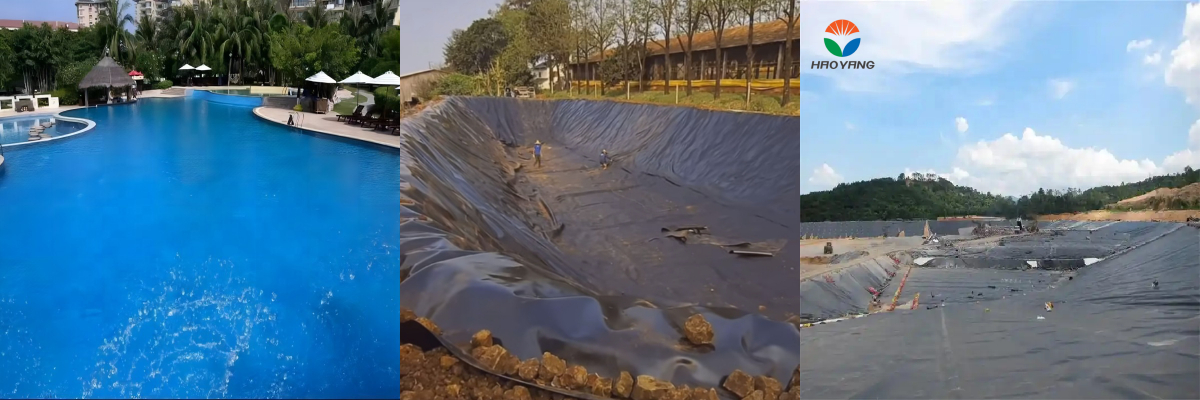
2. Decorative Water Features
Use Case: Artificial lakes, fountains, and swimming pool liners.
Advantages:
Aesthetic appeal with vibrant blue hues mimicking natural water bodies.
Smooth surface prevents biofilm formation.
3. Solar Evaporation Ponds
Use Case: Salt production and lithium extraction facilities.
Advantages:
Reflective blue surface reduces heat absorption, minimizing water loss through evaporation.
Chemical resistance to brine solutions.
4. Landfill Final Covers
Use Case: Exposed landfill caps requiring erosion control and visual screening.
Advantages:
Blue pigment acts as a visual deterrent against unauthorized access.
UV resistance ensures long-term durability in unshaded areas.
5. Mining Leach Pads
Use Case: Secondary containment for cyanide-laden solutions.
Advantages:
Blue coloration aids in leak detection via contrast with surrounding soil.
Puncture resistance handles heavy machinery traffic.
Advantages Over Alternative Materials
1. Thermal Stability vs. Black PVC
Blue PVC’s reduced light absorption minimizes thermal expansion, critical for:
Floating covers in reservoirs.
Exposed landfill caps in arid regions.
2. Aesthetic Flexibility vs. Standard Liners
Customizable shades of blue (e.g., sky blue, navy) match architectural designs or natural landscapes.
3. Algae Control vs. Clear Liners
Light reflection inhibits photosynthesis, reducing maintenance costs in aquaculture by up to 30%.
Environmental Considerations
1. Lifecycle Analysis
Service Life: Blue PVC geomembranes last 15–25 years in aquaculture applications, with minimal degradation.
Recyclability: Post-industrial scrap can be repurposed into drainage boards or traffic cones.
2. Pigment Safety
Organic dyes replace heavy-metal-based pigments, aligning with REACH and RoHS regulations.
3. Carbon Footprint
Production emissions are 15% lower than EPDM alternatives due to lower curing temperatures.
Installation Best Practices
1. Surface Preparation
Subgrades must be free of debris and vegetation. A 50mm layer of geotextile prevents pigment staining from soil.
2. Welding Methods
Hot Air Welding: Ideal for thin gauges (0.5–1.0mm), with temperatures adjusted to 300–350°C.
Dual-Track Seaming: Ensures redundancy in critical applications like landfill covers.
3. Seam Testing
Vacuum Box Test: Detects leaks in welded seams with 95% accuracy.
Electro-Leak Location: Identifies pinholes as small as 0.5mm in diameter.
4. Anchoring
Use concrete ballast blocks or trench backfilling with sandbags to prevent wind uplift in exposed installations.
Case Study: Ornamental Fish Farm in the Mediterranean
A 20-hectare fish farm in Greece installed 1.2mm blue PVC geomembranes for 150+ ponds. Key outcomes:
Algae Reduction: 40% decrease in maintenance cycles compared to clear EPDM liners.
Thermal Control: Water temperatures remained 2–3°C lower than adjacent farms, reducing fish stress.
Aesthetic Appeal: Blue ponds attracted eco-tourism, boosting revenue by 25%.
Challenges and Limitations
1. Color Fading
Prolonged UV exposure may cause slight fading, though pigment stability tests show <10% color loss over 10 years.
2. Cost Premium
Blue PVC costs 5–10% more than standard black variants due to pigment and testing expenses.
3. Chemical Limitations
Not recommended for strong oxidizing agents (e.g., concentrated sulfuric acid).
Conclusion
Blue PVC geomembranes offer a unique blend of functionality and aesthetics, making them indispensable in specialized applications like aquaculture and decorative water features. Their ability to balance thermal stability, chemical resistance, and visual appeal positions them as a premium solution in environmental engineering. While challenges like color fading and cost premiums exist, advancements in pigment technology and recycling initiatives continue to enhance their sustainability profile.