0.5mm LDPE Geomembrane
1.Excellent Flexibility – Easily adapts to irregular surfaces for convenient installation.
2.Good Chemical Resistance – Withstands acids, alkalis, and salts, suitable for various environments.
3.Eco-Friendly & Non-Toxic – Made from high-quality LDPE, safe for soil and water.
4.Superior Seepage Control – Low permeability effectively prevents leakage and contamination.
5.Cost-Effective – Affordable option for large-scale engineering projects.
0.5mm LDPE Geomembrane
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) geomembranes have become essential materials in modern environmental and civil engineering projects due to their excellent sealing properties and adaptability. Among the various thickness options available, the 0.5mm LDPE geomembrane stands out for its balance between flexibility, cost, and effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of projects requiring medium-duty waterproofing and containment solutions.
Material Characteristics
LDPE is a thermoplastic made from the polymerization of ethylene. Compared to HDPE, LDPE has a lower density and greater ductility, which results in improved flexibility and elongation. The 0.5mm thickness provides a lightweight yet sufficiently durable barrier layer that can be easily transported, handled, and installed without heavy machinery.
This geomembrane is manufactured through blown film or extrusion technology, ensuring consistent thickness, smooth surface texture, and strong tensile strength. It is commonly produced using 100% virgin LDPE resin, enhancing its mechanical properties and environmental safety.
Key Benefits
1. High Flexibility and Conformability
One of the defining features of 0.5mm LDPE geomembrane is its ability to conform to uneven ground surfaces. This makes it especially useful in applications where the substrate is rocky, sloped, or irregular. Its softness allows it to wrap around corners and edges with minimal risk of tearing, which is particularly useful in agricultural ponds or small landfill cells.
2. Resistance to Chemicals and UV
LDPE geomembranes offer a good level of resistance to many chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts. This makes the 0.5mm version suitable for use in environments where chemical exposure is a concern, such as wastewater treatment sites or industrial effluent containment. When UV-stabilized additives are included during production, the material also resists degradation from sunlight, enhancing its outdoor lifespan.
3. Environmental Safety
LDPE is considered a relatively eco-safe material. It does not leach harmful substances into soil or water and is often approved for use in applications involving potable water or aquaculture. This feature ensures that the geomembrane can be deployed in sensitive ecological settings without posing a threat to local flora and fauna.
4. Waterproofing Performance
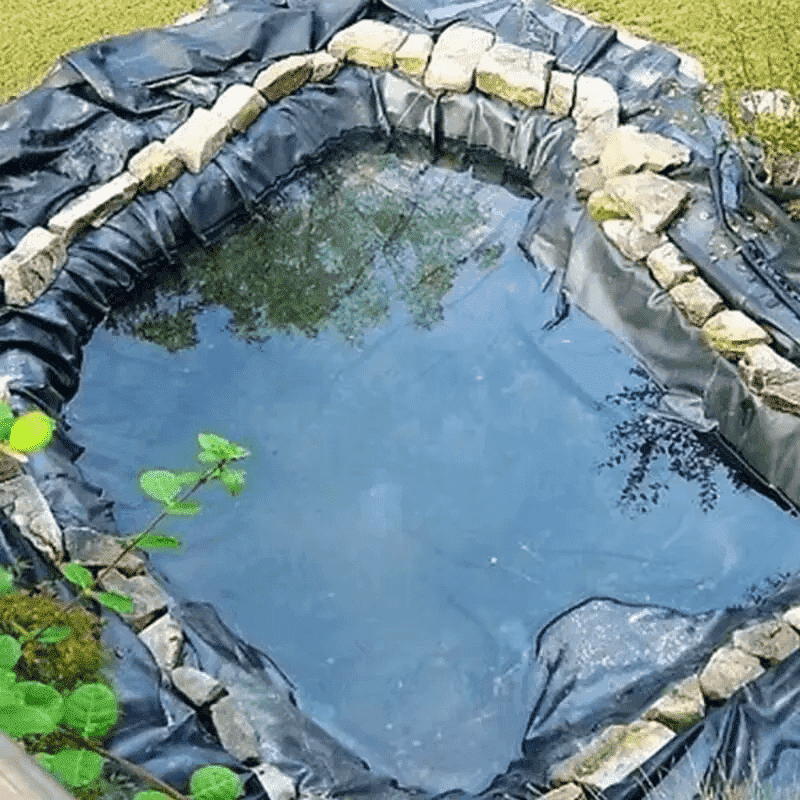
Although thinner than many industrial-grade liners, the 0.5mm LDPE sheet still provides reliable waterproofing. It acts as an effective barrier to liquids and gases, preventing seepage into surrounding soil and groundwater. This is critical in projects such as irrigation canals, fish ponds, and reservoirs, where water conservation is a primary objective.
5. Ease of Installation and Lower Cost
Thanks to its light weight, this type of geomembrane can be installed with minimal labor and equipment. It can be manually unrolled and positioned, and it’s suitable for thermal or chemical welding to ensure seamless joints. These installation advantages, combined with its relatively low material cost, make it a practical solution for projects with tight budgets or short timelines.
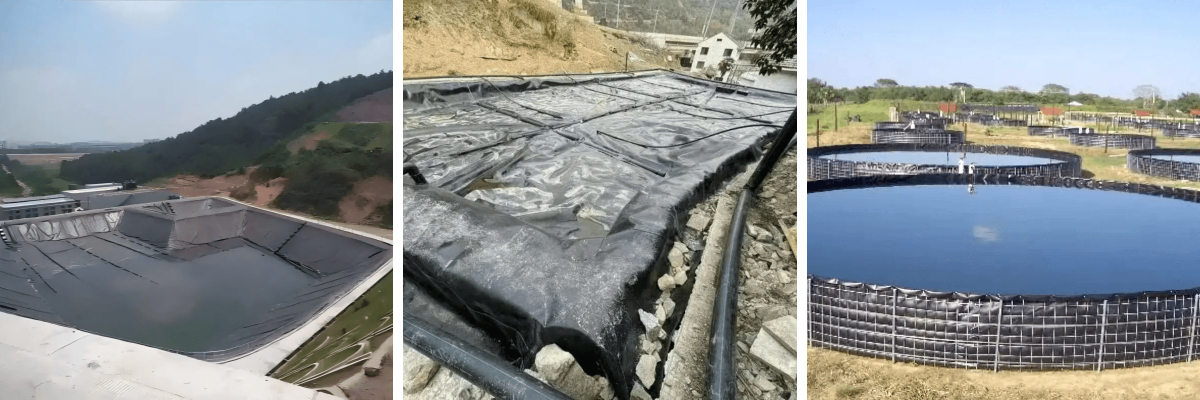
Common Applications
The versatility of the 0.5mm LDPE geomembrane lends itself to numerous uses in both environmental protection and infrastructure development:
Agricultural Water Storage: Used in lining irrigation ditches, artificial lakes, and water tanks.
Aquaculture: Provides a clean, non-toxic barrier in fish or shrimp ponds, helping maintain water quality.
Landfill Capping: Employed as a surface liner to limit rainwater infiltration and gas emission.
Mining Operations: Acts as a lining system in tailings ponds and heap leach pads.
Secondary Containment: Used beneath chemical storage tanks or pipelines to catch potential leaks.
Temporary Covers: Utilized in construction projects for temporary weather protection or containment.
Durability and Maintenance
Although thinner geomembranes are more prone to physical damage compared to thicker ones, the 0.5mm LDPE version still provides reasonable durability under normal use conditions. For added protection, a layer of geotextile fabric is often installed above and/or below the membrane to guard against punctures from sharp stones or debris.
Maintenance of LDPE geomembrane-lined facilities is relatively simple. Periodic inspections can help identify potential damage, which can typically be repaired using heat welding or patching kits, minimizing downtime and cost.
Comparison with Other Materials
While LDPE offers several unique advantages, it’s important to compare it with other geomembrane types for better decision-making. For instance, HDPE geomembranes are more rigid and chemical-resistant, making them better suited for demanding applications like hazardous waste containment. However, LDPE’s superior flexibility gives it the edge in smaller, more intricate installations where adaptability and ease of handling are key.
PVC is another alternative known for its flexibility, but it tends to have a shorter service life and may leach plasticizers over time. EPDM and TPO liners are widely used in roofing or decorative pond applications, but they are generally more expensive and may require specialized installation.
Sustainability Perspective
With increasing attention to sustainable engineering practices, the recyclability and relatively low carbon footprint of LDPE materials offer additional benefits. Some manufacturers now offer LDPE geomembranes made partially from recycled content, helping reduce environmental impact without compromising performance. When decommissioned, these liners can often be collected and repurposed, further extending their lifecycle.
No. | Item | Unit | Index | ||||||||
1 | Thickness | mm | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.00 |
2 | Density | g/cm3 | ≧0.940 | ||||||||
3 | Tensile yield strength | N/mm | ≧4 | ≧7 | ≧10 | ≧13 | ≧16 | ≧20 | ≧26 | ≧33 | ≧40 |
4 | Tensile breaking strength | N/mm | ≧6 | ≧10 | ≧15 | ≧20 | ≧25 | ≧30 | ≧40 | ≧50 | ≧60 |
5 | Yield elongation | % | - | - | - | ≧11 | |||||
6 | Break Elongation | % | ≧600 | ||||||||
7 | Right-angle Tearing strength | N | ≧34 | ≧56 | ≧84 | ≧115 | ≧140 | ≧170 | ≧225 | ≧280 | ≧340 |
8 | Puncture strength | N | ≧72 | ≧120 | ≧180 | ≧240 | ≧300 | ≧360 | ≧480 | ≧600 | ≧720 |
9 | Carbon black content | % | 2.0~3.0 | ||||||||
10 | Dispersion of carbon black | - | There is not more than one level 3 in 10 data, and level 4 and level 5 are not allowed to exist. | ||||||||
11 | Oxidation induction time | min | ≧60 | ||||||||
12 | Low temperature impact embrittlement properties | - | Pass | ||||||||
13 | Water vapor permeability coefficient | g.cm/ (cm2.s.Pa) | ≦1.0*10-13 | ||||||||
14 | Dimensional stability | % | ±2.0
| ||||||||
Note | Technical performance indicators for thickness specifications not listed in the table are required to be performed by interpolation. | ||||||||||
The 0.5mm LDPE geomembrane presents an excellent solution for projects requiring moderate waterproofing with maximum flexibility and cost-efficiency. Its chemical resistance, ease of deployment, and environmental friendliness make it well-suited to various sectors including agriculture, aquaculture, waste management, and infrastructure. While it may not replace thicker or more specialized liners in all applications, it serves as a reliable and practical option for countless mid-scale needs.
For engineers, contractors, and environmental planners looking for a balance between performance and affordability, the 0.5mm LDPE geomembrane continues to prove its value across the globe.