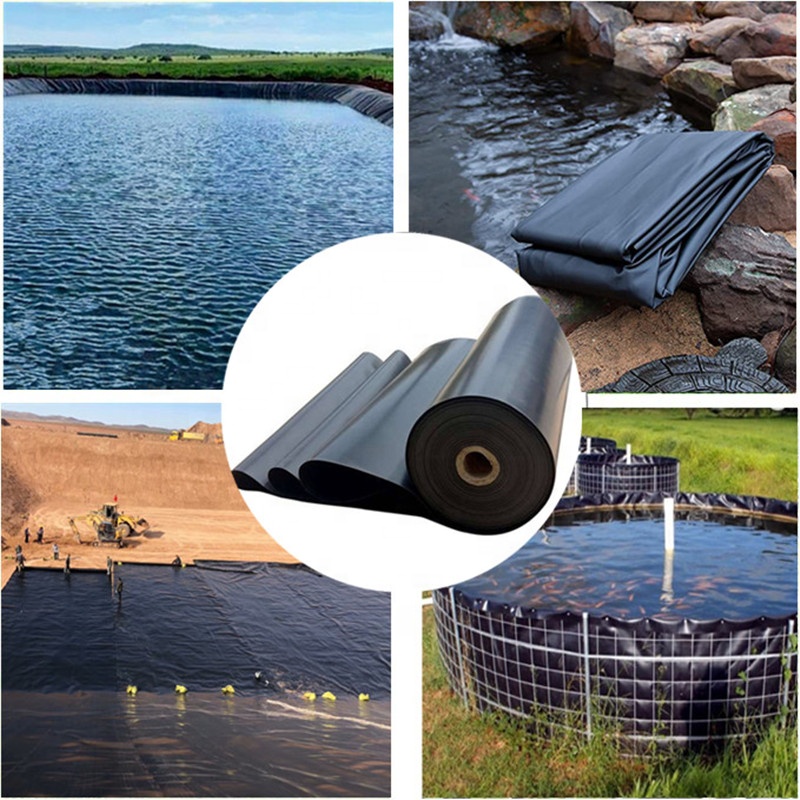
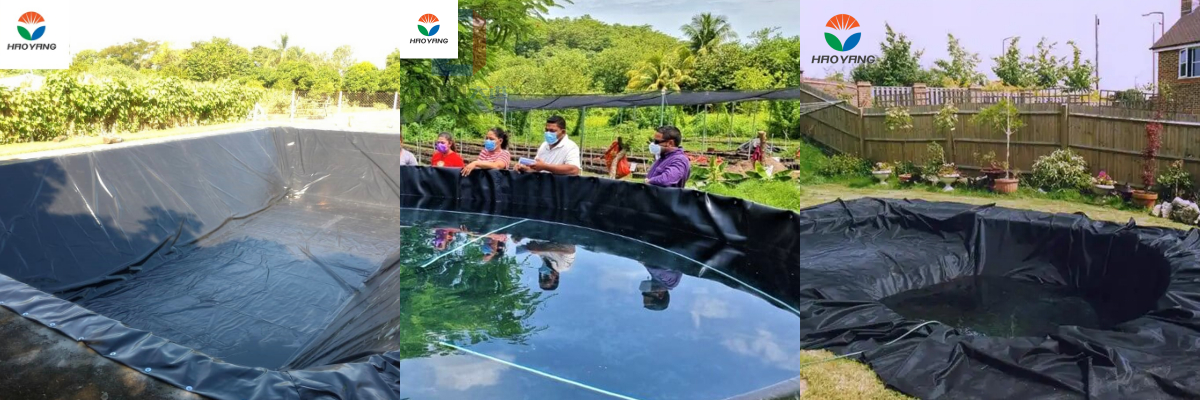
Geomembrane For Pond Liners
Unmatched Seepage Prevention
Geomembranes provide a near-impermeable barrier, reducing water loss by up to 99% compared to unlined ponds, critical for water-scarce regions.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Despite higher upfront costs, geomembranes offer 30–50% lower lifecycle expenses due to reduced maintenance and extended service life (25–50 years).
Adaptability to Challenging Conditions
Their flexibility and chemical resistance make geomembranes suitable for extreme environments, from Arctic tundra to desert climates and corrosive industrial settings.
Geomembrane for Pond Liner: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Performance
Introduction
Geomembranes have revolutionized pond liner technology, offering a durable, cost-effective, and versatile solution for water containment across industries. As synthetic polymer barriers, geomembranes prevent seepage, contamination, and structural failure in applications ranging from agricultural irrigation ponds to industrial wastewater reservoirs. This article explores the technical specifications, performance metrics, and real-world applications of geomembranes, supported by empirical data and comparative analyses.
Material Composition and Types
Geomembranes are manufactured from polymer resins such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). Each material offers distinct advantages:
| Material | Thickness Range (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Puncture Resistance (N) | UV Resistance (Years) | Chemical Resistance |
HDPE | 0.5–3.0 | 20–40 | 400–600 | 5–10 | Excellent (acids/alkalis) |
LLDPE | 0.5–2.0 | 15–30 | 300–500 | 3–7 | Good (moderate chemicals) |
PVC | 0.8–2.0 | 18–35 | 350–550 | 2–5 | Fair (limited acids) |
EPDM | 1.0–2.5 | 10–20 | 250–400 | 10+ | Poor (hydrocarbons) |
Key Performance Attributes
Hydraulic Barrier Efficiency
Geomembranes achieve hydraulic conductivity as low as 1×10⁻¹⁴ m/s, far exceeding the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requirement of ≤1×10⁻⁷ cm/s for landfill liners. HDPE geomembranes, for example, demonstrate a seepage rate of <0.001 L/m²/day in field tests, outperforming compacted clay by 99.9%.Chemical and UV Resistance
HDPE and LLDPE geomembranes resist degradation from agricultural chemicals, hydrocarbons, and saline environments. A 2021 study by the International Association of Geosynthetic Installers (IAGI) found that HDPE liners exposed to 50,000 ppm TDS solutions retained >98% of their original tensile strength after 10 years.Mechanical Durability
Geomembranes withstand high stress and deformation. HDPE variants exhibit a 200% elongation at break, enabling them to conform to uneven substrates without cracking. In a 2022 test, a 1.5mm HDPE liner survived a 10,000-hour accelerated aging cycle without punctures, simulating 25 years of field exposure.
Applications Across Industries
Agricultural and Aquaculture Ponds
Irrigation Reservoirs: HDPE liners reduce water loss by 95% compared to unlined ponds, critical in arid regions.
Fish Farms: LLDPE liners provide flexibility for floating cage systems, withstanding tidal forces and fish activity.
Industrial Wastewater Management
Mining Leach Ponds: HDPE liners withstand pH extremes (2–12) and heavy metal concentrations up to 5,000 mg/L.
Power Plant Ash Ponds: 2.0mm HDPE liners prevent groundwater contamination from coal ash leachate.
Environmental Remediation
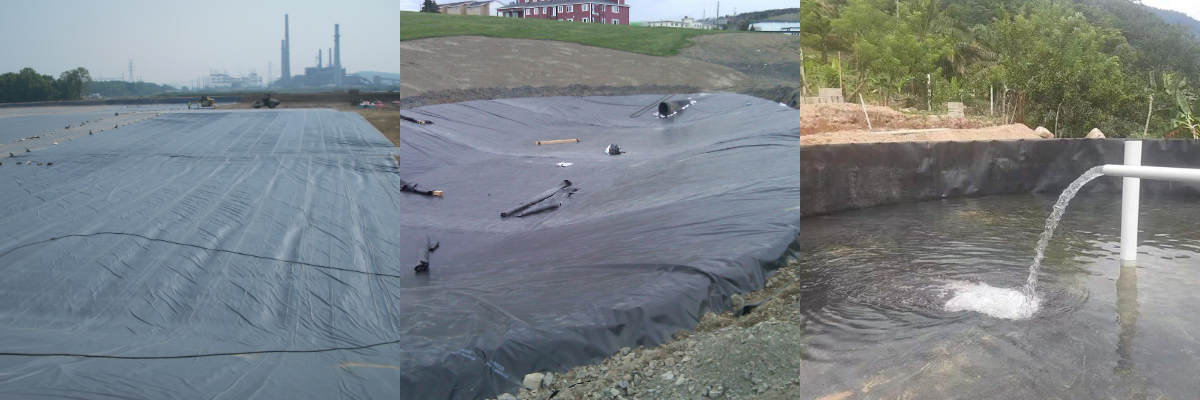
Capped Landfills: Multi-layer HDPE systems (1.5mm primary + 1.0mm secondary) achieve <1% gas emission leakage.
Stormwater Basins: PVC liners resist UV degradation for 5+ years in open-air applications.
Installation and Cost Considerations
Geomembranes offer significant advantages over traditional materials like concrete or clay:
| Parameter | Geomembrane (HDPE) | Compacted Clay (1.5m) | Concrete (150mm) |
Installation Speed | 500–800 m²/day | 200–300 m²/day | 300–400 m²/day |
Material Cost ($/m²) | 1.2–2.5 | 2.0–3.0 | 3.5–5.0 |
Lifecycle Cost (30 Years) | $4.5–7.0/m² | $9.0–12.0/m² | $8.5–11.5/m² |
Carbon Footprint (kg CO₂e/m²) | 2.5–4.0 | 6.0–8.0 | 5.5–7.5 |
Case Study: Aquaculture Pond in Southeast Asia
A 10-hectare shrimp farm in Vietnam replaced its unlined earthen pond with a 1.2mm HDPE geomembrane. Key outcomes:
Water Savings: Reduced seepage from 30% to <2%, saving 45,000 m³/year.
Yield Increase: Stable water chemistry boosted shrimp survival rate from 60% to 85%.
Cost Recovery: Initial investment of $120,000 recouped in 3 years through higher yields and lower maintenance.
Comparative Analysis: Geomembrane vs. Traditional Liners
| Factor | Geomembrane | Concrete | |
Seepage Control | 99.9%+ efficiency | 90–95% efficiency | 95–98% efficiency |
Installation Time | 3–5 days (10,000 m²) | 10–14 days | 7–10 days |
Maintenance | Minimal | Frequent compaction | Periodic crack repair |
Environmental Impact | Low (recyclable) | High (soil disruption) | Moderate (cement production) |
Conclusion
Geomembranes represent a paradigm shift in pond liner technology, offering unparalleled performance in water containment, chemical resistance, and cost efficiency. Their versatility across industries, coupled with measurable environmental benefits, ensures their dominance in modern infrastructure projects. As regulatory standards tighten and sustainability demands grow, geomembranes will remain a cornerstone of responsible resource management.