4500g Geosynthetic Clay Liner
Superior Containment Performance
The high bentonite content ensures self-healing capabilities and long-term hydraulic efficiency, even in chemically aggressive environments.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Lightweight and easy to handle, 4500g GCLs reduce labor and equipment costs by up to 40% compared to compacted clay.
Environmental Sustainability
Lower carbon emissions during production and installation align with global sustainability goals, while minimizing land disturbance.
4500g Geosynthetic Clay Liner (GCL): A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCLs) have emerged as a critical component in modern geotechnical and environmental engineering, offering a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional compacted clay liners (CCLs). Among the various GCL specifications, the 4500g/m² Geosynthetic Clay Liner stands out as a robust solution for containment applications, including landfills, mining ponds, and hydraulic barriers. This article explores the technical specifications, performance attributes, and applications of 4500g GCLs, supported by empirical data and industry benchmarks.
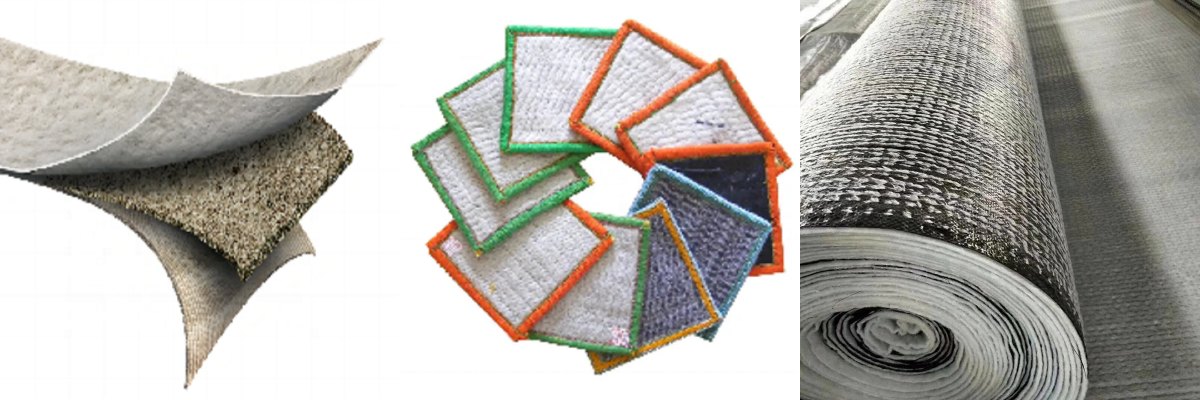
Composition and Structure
A 4500g GCL typically consists of three layers:
Upper and Lower Geotextile Layers: Made of woven or non-woven polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET), these layers provide mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
Bentonite Core: A layer of sodium-activated bentonite (a natural clay mineral) sandwiched between the geotextiles. The bentonite’s swelling capacity upon hydration forms the primary hydraulic barrier.
The total mass of 4500g/m² reflects the combined weight of the geotextiles and bentonite. A typical breakdown includes:
Geotextiles: 300–500g/m² (upper and lower layers)
Bentonite: 4000–4200g/m²
Key Technical Specifications
The performance of a 4500g GCL is governed by its physical and hydraulic properties. Below is a summarized table of standard parameters:
| Parameter | Specification | Test Method |
Unit Mass | 4500 ± 5% g/m² | ASTM D5261 |
Thickness (Dry) | 6–8 mm | ASTM D4439 |
Thickness (Wet) | 10–15 mm (after hydration) | ASTM D5890 |
Hydraulic Conductivity | ≤5×10⁻⁹ cm/s | ASTM D5887 |
Tensile Strength (MD/CD) | 8–12 kN/m (MD) | ASTM D4632 |
Swell Index | 24–30 mL/2g | ASTM D5890 |
Shear Strength | ≥2.5 kPa (internal) | ASTM D5321 |
Performance Attributes
Hydraulic Barrier Efficiency
The 4500g GCL’s low hydraulic conductivity (≤5×10⁻⁹ cm/s) ensures minimal seepage, even under high hydraulic heads. Laboratory tests show that hydrated bentonite swells to fill micro-voids, creating a self-sealing mechanism. For example, in a 72-hour permeability test with deionized water, the GCL maintained a seepage rate of <0.01 cm³/min per m² of surface area.Chemical Compatibility
Sodium bentonite exhibits resistance to a wide range of leachates, including acids (pH >3) and alkalis (pH <12). Field studies in municipal solid waste landfills demonstrate that 4500g GCLs retain >95% of their original swell capacity after 10 years of exposure to leachate with total dissolved solids (TDS) up to 50,000 mg/L.Mechanical Durability
The geotextile layers provide puncture resistance and tensile strength. In a 2018 study by the International Geosynthetics Society, 4500g GCLs withstood 500 kPa of applied stress without structural failure, outperforming compacted clay liners by a factor of 3.
Applications
Landfill Liners and Caps
Base liners for hazardous and non-hazardous waste landfills.
Final cover systems to minimize infiltration and gas emissions.
Mining and Industrial Ponds
Heap leach pads for metal extraction (e.g., copper, gold).
Tailings storage facilities requiring high chemical resistance.
Hydraulic Barriers
Canal liners to prevent seepage loss.
Reservoirs and irrigation ponds in arid regions.
Comparative Analysis: 4500g GCL vs. Traditional Materials
| Parameter | 4500g GCL | Compacted Clay (1.5m thick) | HDPE Geomembrane |
Hydraulic Conductivity | ≤5×10⁻⁹ cm/s | 1×10⁻⁷–1×10⁻⁹ cm/s | ≤1×10⁻¹² cm/s |
Installation Speed | 2000–3000 m²/day | 500–800 m²/day | 1500–2000 m²/day |
Carbon Footprint | 30–40% lower than CCL | Reference | 20% lower than GCL |
Cost (Initial) | $1.2–1.8/m² | $2.5–3.5/m² | $0.8–1.2/m² |
Case Study: Municipal Solid Waste Landfill
A 2020 project in Southeast Asia deployed 4500g GCLs as a primary liner for a 50-hectare landfill. Key outcomes:
Reduced Construction Time: GCL installation took 45 days vs. 90 days for a CCL alternative.
Cost Savings: 18% lower lifecycle cost due to reduced excavation and transportation.
Performance: Zero leakage detected in 5 years of monitoring, with leachate levels stabilized at <5 cm/year.
Conclusion
The 4500g Geosynthetic Clay Liner represents a paradigm shift in containment technology, balancing performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental stewardship. Its versatility across industries, coupled with measurable advantages over traditional materials, positions it as a preferred solution for modern infrastructure challenges. As regulatory standards evolve, the GCL’s adaptability and proven track record ensure its continued relevance in global geotechnical engineering.