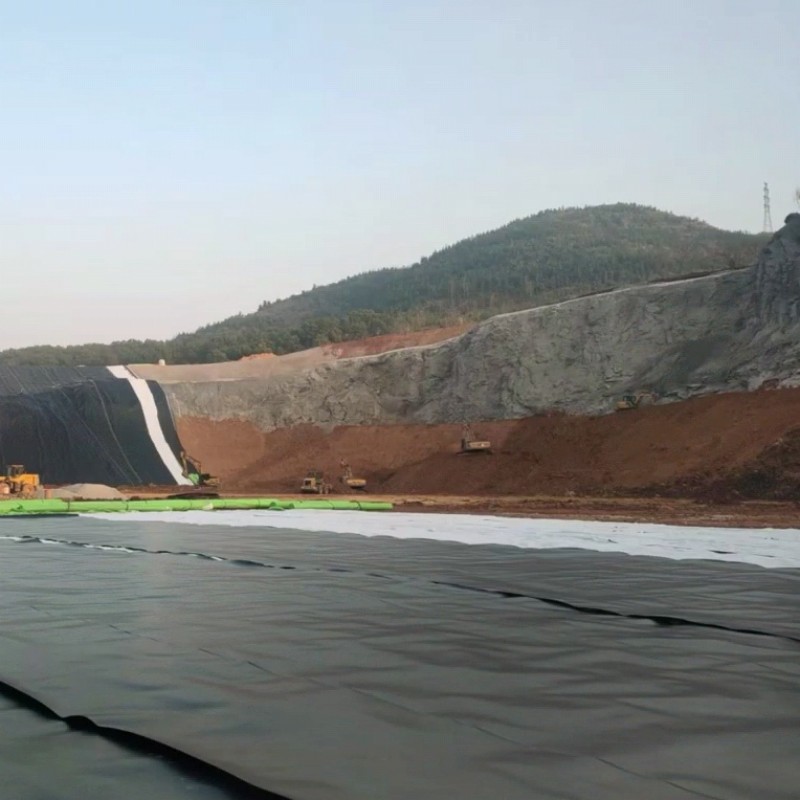
0.75mm HDPE Dam Liner
1. Excellent impermeability
Effectively prevents water seepage, maintaining reliable reservoir and pond performance.
2. Superior chemical resistance
Resists acids, alkalis, salts, and other chemicals, making it suitable for diverse water conditions.
3. UV and weather resistance
Formulated to withstand sunlight and temperature fluctuations, ensuring long-term outdoor durability.
4. Flexible and easy to install
Adapts well to uneven surfaces and complex shapes, simplifying installation and reducing labor costs.
5. Cost-effective solution
Offers an ideal balance of performance and affordability, especially for medium-duty projects.
0.75mm HDPE Dam Liner
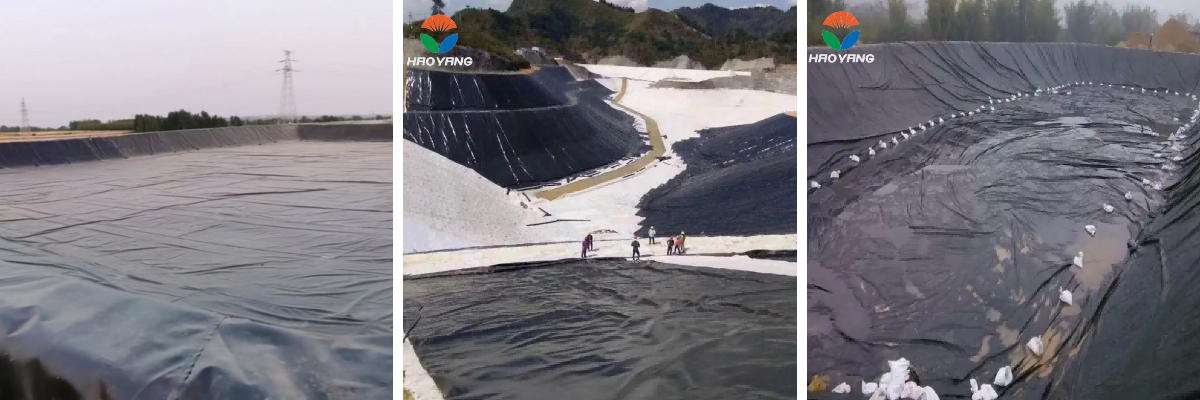
In modern water conservation, irrigation systems, mining operations, and environmental protection projects, the choice of lining material plays a decisive role in ensuring long-term performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Among the various options available, the 0.75mm HDPE dam liner has become widely recognized for its balance of strength, flexibility, and economic efficiency.
What is a 0.75mm HDPE Dam Liner?
HDPE stands for High-Density Polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer made from petroleum known for its high strength-to-density ratio and excellent chemical resistance. A 0.75mm HDPE dam liner is a geomembrane sheet with a nominal thickness of 0.75 millimeters, specifically engineered to serve as a water-impermeable barrier in dam, pond, and reservoir projects.
Though relatively thin compared to thicker geomembranes (such as 1.0mm or 1.5mm liners), the 0.75mm thickness offers a cost-effective solution without compromising essential performance. It is suitable for applications where ground settlement is minimal, or where the liner is protected from direct mechanical damage.
Key Advantages
1. Effective Water Seepage Prevention
The primary function of any dam liner is to prevent water loss through seepage. HDPE has an inherently low permeability, and even at a thickness of 0.75mm, the liner forms a reliable barrier that minimizes water leakage, preserving valuable resources and ensuring efficient reservoir management.
2. Outstanding Chemical Resistance
Water in reservoirs and ponds may contain dissolved minerals, salts, or chemicals. HDPE resists chemical attack from a broad range of substances, including acids, alkalis, and salts. This makes it suitable for irrigation dams, fish ponds, and even certain industrial wastewater applications.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability
At 0.75mm thickness, the dam liner maintains good flexibility, making it easier to conform to irregular substrates and complex basin shapes. This adaptability reduces the risk of voids or folds that could weaken the liner over time.
4. UV and Weather Resistance
HDPE geomembranes are formulated with carbon black and stabilizers to resist degradation under prolonged exposure to sunlight and fluctuating temperatures. This UV stability ensures that the liner retains its physical properties over years of outdoor service.
5. Economic Efficiency
One of the main reasons project owners choose a 0.75mm liner is its cost advantage. Compared to thicker liners, it requires less raw material, making it more affordable. When combined with proper installation and protection layers (such as geotextiles or soil cover), it provides reliable long-term performance at a lower upfront investment.
Applications
The 0.75mm HDPE dam liner is suitable for a range of projects where moderate mechanical demands and effective seepage control are required. Common applications include:
Irrigation ponds and small agricultural dams
To store water for crops, livestock, or aquaculture.Decorative lakes and landscaping water features
Where aesthetics and water retention are both important.Rainwater harvesting reservoirs
Providing secure storage for collected rainwater.Secondary containment
Such as beneath storage tanks to prevent environmental contamination.Evaporation ponds and leachate ponds
In industrial or municipal waste management.
While thicker liners (e.g., 1.0mm, 1.5mm) are generally used for landfill base liners or high-load mining tailings dams, the 0.75mm liner remains popular for lighter-duty applications, especially where cost control is critical.
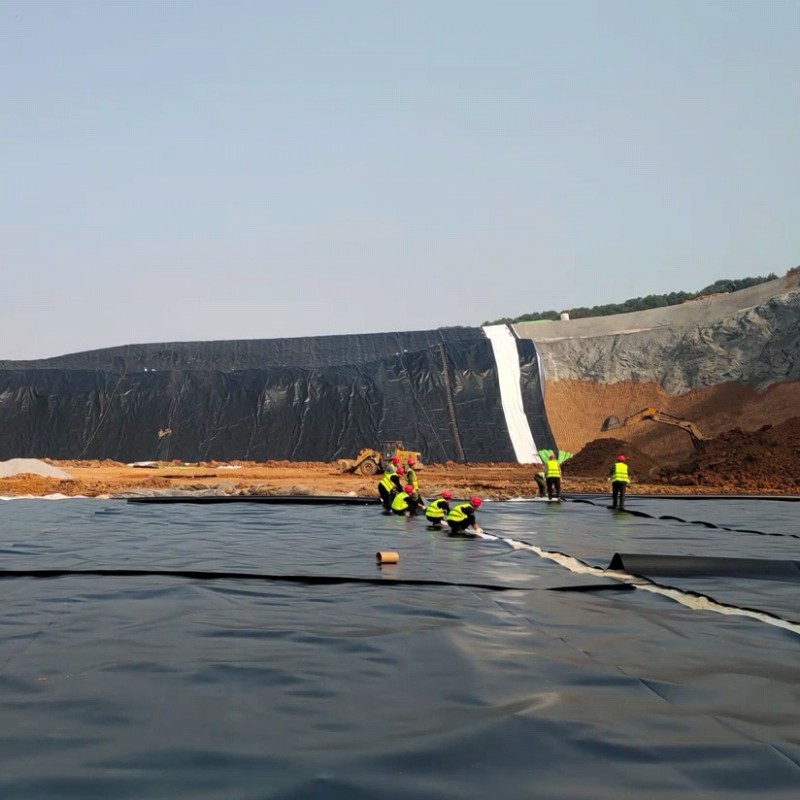
Installation Considerations
Achieving optimal performance from a 0.75mm HDPE dam liner requires correct installation. Important points include:
Surface Preparation:
The substrate should be free of sharp stones, roots, or debris that might puncture the liner.Seaming:
Panels are joined using hot wedge welding or extrusion welding to ensure watertight seams.Protection Layers:
Geotextiles are often placed below and/or above the liner to protect it from puncture and mechanical damage.Anchor Trenches:
The liner edges should be securely anchored in trenches around the perimeter to prevent uplift by wind or water pressure.Qualified Installers:
Engaging experienced geomembrane installers reduces the risk of faulty seams or poor surface preparation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
HDPE is chemically inert and does not leach harmful substances into the environment. At the end of its service life, HDPE geomembrane can be recycled into other plastic products, reducing landfill waste. Its long lifespan (often exceeding 20 years under favorable conditions) also means fewer replacements, conserving materials and reducing project life cycle costs.
Comparison with Other Liners
When selecting a dam liner, project managers may compare HDPE with other geomembrane materials such as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene), or EPDM rubber. Each has its strengths:
PVC:
Greater flexibility at lower temperatures, but less UV and chemical resistance.LLDPE:
Higher flexibility than HDPE, useful for very complex shapes, but generally slightly lower puncture resistance.EPDM:
Excellent elasticity and UV resistance but higher cost.
HDPE is often favored where cost, chemical resistance, and UV stability are prioritized.
No. | Item | Unit | Index | ||||||||
1 | Thickness | mm | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.00 |
2 | Density | g/cm3 | ≧0.940 | ||||||||
3 | Tensile yield strength | N/mm | ≧4 | ≧7 | ≧10 | ≧13 | ≧16 | ≧20 | ≧26 | ≧33 | ≧40 |
4 | Tensile breaking strength | N/mm | ≧6 | ≧10 | ≧15 | ≧20 | ≧25 | ≧30 | ≧40 | ≧50 | ≧60 |
5 | Yield elongation | % | - | - | - | ≧11 | |||||
6 | Break Elongation | % | ≧600 | ||||||||
7 | Right-angle Tearing strength | N | ≧34 | ≧56 | ≧84 | ≧115 | ≧140 | ≧170 | ≧225 | ≧280 | ≧340 |
8 | Puncture strength | N | ≧72 | ≧120 | ≧180 | ≧240 | ≧300 | ≧360 | ≧480 | ≧600 | ≧720 |
9 | Carbon black content | % | 2.0~3.0 | ||||||||
10 | Dispersion of carbon black | - | There is not more than one level 3 in 10 data, and level 4 and level 5 are not allowed to exist. | ||||||||
11 | Oxidation induction time | min | ≧60 | ||||||||
12 | Low temperature impact embrittlement properties | - | Pass | ||||||||
13 | Water vapor permeability coefficient | g.cm/ (cm2.s.Pa) | ≦1.0*10-13 | ||||||||
14 | Dimensional stability | % | ±2.0
| ||||||||
Note | Technical performance indicators for thickness specifications not listed in the table are required to be performed by interpolation. | ||||||||||
The 0.75mm HDPE dam liner represents an effective and affordable solution for water storage, irrigation, aquaculture, and secondary containment applications. Its combination of low permeability, chemical resistance, flexibility, and UV stability makes it a trusted choice for engineers, farmers, and environmental managers worldwide.
While proper installation and site conditions determine its ultimate lifespan, a 0.75mm HDPE liner, when well designed and protected, can offer many years of reliable service. Balancing cost-efficiency with performance, it remains a practical option for many medium-duty projects, contributing to sustainable water management and environmental protection.