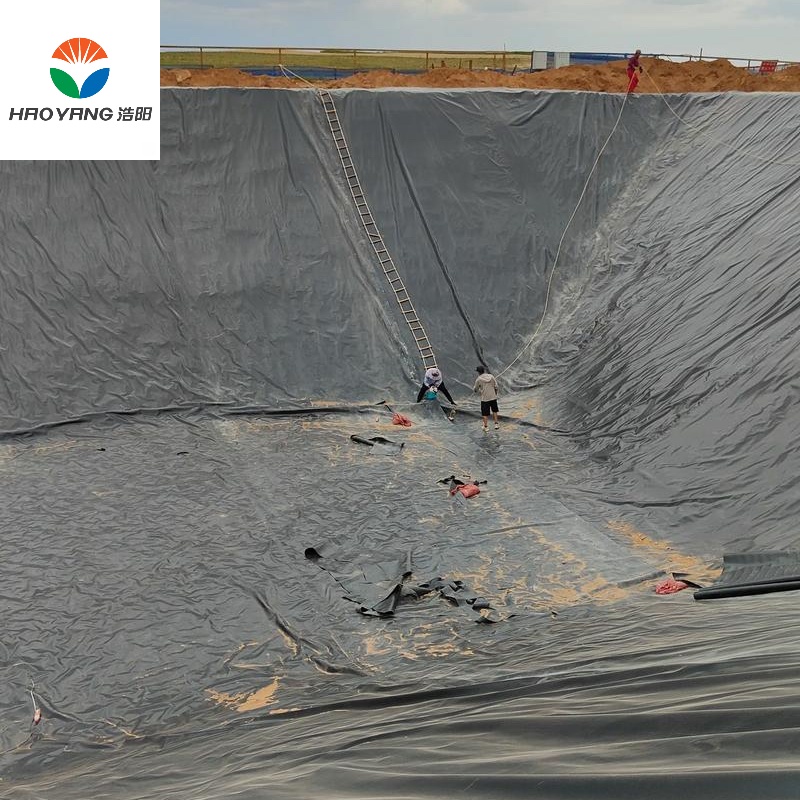
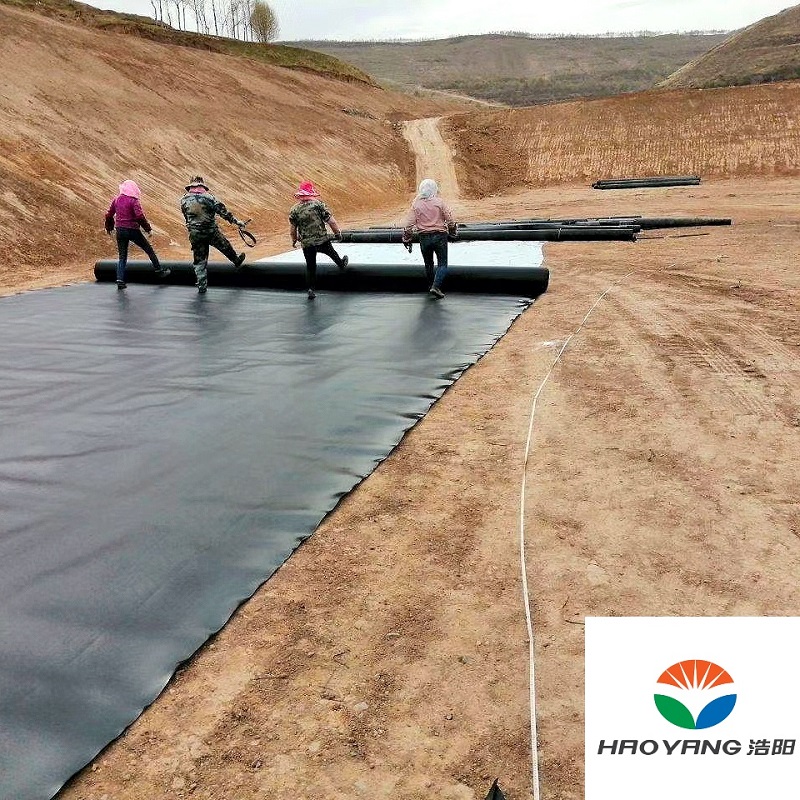
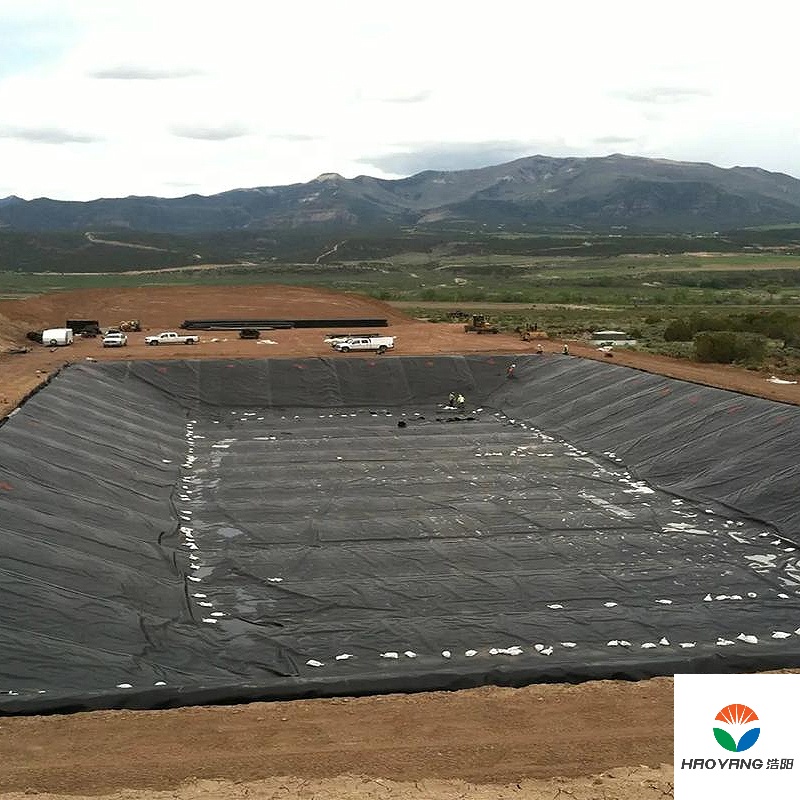
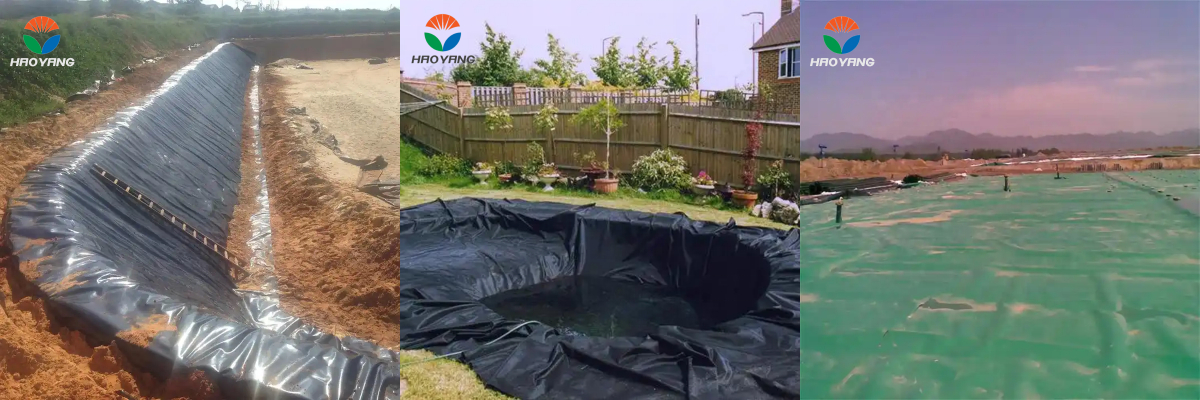
2mm LLDPE Geomembrane Liner
Unmatched Flexibility and Durability: The 700% elongation capacity allows the liner to withstand settlement, thermal expansion, and seismic activity without cracking.
Superior Chemical Resistance: Ideal for aggressive environments, including acidic leach pads and hydrocarbon storage.
Cost-Effective Longevity: Balanced thickness minimizes material costs while ensuring decades of reliable performance.
2mm LLDPE Geomembrane Liner: A Comprehensive Overview
Geomembrane liners play a pivotal role in modern environmental engineering, offering reliable containment solutions for industries ranging from mining and agriculture to waste management and water conservation. Among the various types of geomembranes, 2mm Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) liners have emerged as a versatile choice due to their balance of durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. This article explores the technical specifications, applications, and advantages of 2mm LLDPE geomembrane liners, supported by performance data and practical insights.
1. Introduction to LLDPE Geomembranes
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer derived from the polymerization of ethylene. Its molecular structure, characterized by short linear chains with occasional branches, imparts superior flexibility, tensile strength, and resistance to environmental stress cracking compared to traditional Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). The 2mm thickness strikes an optimal balance between mechanical robustness and ease of installation, making it suitable for a wide range of containment applications.
2. Technical Specifications of 2mm LLDPE Geomembrane
The performance of a geomembrane is determined by its physical, mechanical, and chemical properties. Below is a detailed breakdown of key parameters for 2mm LLDPE liners:
Table 1: Physical and Mechanical Properties
| Parameter | Specification | Test Method |
Thickness (nominal) | 2.0 mm ± 5% | ASTM D5199 |
Density | 0.93–0.94 g/cm³ | ASTM D1505 |
Tensile Yield Strength | ≥ 20 MPa (MD/TD) | ASTM D638 |
Elongation at Break | ≥ 700% (MD/TD) | ASTM D638 |
Puncture Resistance | ≥ 400 N | ASTM D4833 |
Carbon Black Content | 2–3% (UV stabilization) | ASTM D1603 |
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) | ≥ 300 hours | ASTM D1693 (Condition B) |
Hydrostatic Resistance | > 100 m (water head) | ASTM D5385 |
Key Insights from the Table:
Thickness Consistency: The 2mm specification adheres to strict tolerances, ensuring uniform performance across large-scale installations.
Flexibility: The elongation-at-break value (>700%) allows the liner to conform to irregular substrates without tearing.
UV Resistance: Carbon black additives (2–3%) provide long-term protection against ultraviolet degradation, critical for exposed applications.
Chemical Resistance: LLDPE’s inertness makes it suitable for contact with acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons (see Section 4 for details).
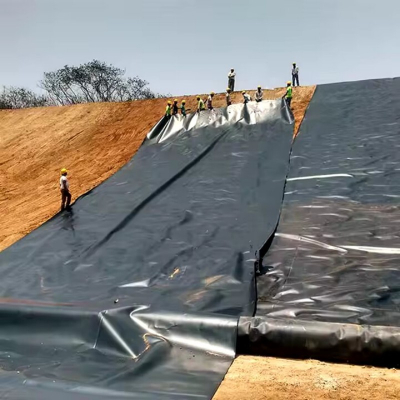
3. Applications of 2mm LLDPE Geomembrane Liners
The adaptability of 2mm LLDPE liners is reflected in their diverse applications:
3.1 Mining and Mineral Processing
Heap Leach Pads: Containment of cyanide or acid solutions in gold and copper extraction.
Tailings Dams: Prevention of seepage from mineral waste storage.
Process Ponds: Lining for settling ponds and leachate collection systems.
3.2 Water and Wastewater Management
Reservoirs and Canals: Reduction of seepage losses in irrigation and drinking water projects.
Sewage Lagoons: Odor control and groundwater protection in municipal wastewater facilities.
Aquaculture Ponds: Maintenance of water quality in fish farming operations.
3.3 Environmental Protection
Landfill Liners: Primary and secondary barriers in municipal solid waste (MSW) and hazardous waste landfills.
Capping Systems: Cover systems to minimize rainwater infiltration and gas emissions.
Coal Ash Ponds: Containment of coal combustion residuals (CCR) in power plants.
3.4 Agriculture
Irrigation Ponds: Water storage for drought-prone regions.
Animal Waste Lagoons: Manure management in dairy and poultry farms.
4. Chemical and Environmental Resistance
LLDPE’s chemical inertness is a cornerstone of its performance. The material exhibits resistance to:
Acids: Sulfuric acid (up to 30% concentration), hydrochloric acid (up to 20%).
Alkalis: Sodium hydroxide (up to 50%).
Hydrocarbons: Diesel, jet fuel, and crude oil (short-term exposure).
Salts: Seawater and brine solutions.
However, prolonged exposure to solvents (e.g., toluene, xylene) or oxidizing agents (e.g., concentrated nitric acid) may cause swelling or degradation. Site-specific compatibility testing is recommended for aggressive chemical environments.
5. Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation is critical to the longevity of a geomembrane system. Key steps include:
5.1 Site Preparation
Subgrade Preparation: Remove sharp objects, vegetation, and debris. Compact soil to achieve a smooth, uniform surface.
Slope Stability: Ensure slopes do not exceed 3:1 (horizontal:vertical) to prevent liner slippage.
5.2 Welding and Seaming
Thermal Welding: Use automated or manual wedge welders for seams. Test welds regularly using peel and shear tests.
Seam Overlap: Maintain a minimum 100mm overlap for extrusion welding or 75mm for tape seams.
5.3 Temperature Control
Installation Temperature: LLDPE becomes brittle below -40°C and pliable above 80°C. Avoid installation in extreme cold or direct sunlight.
5.4 Protection and Anchorage
Protection Layers: Cover with geotextile or soil to prevent UV exposure and mechanical damage.
Anchorage: Secure edges with trenching, concrete anchors, or ballast.
5.5 Inspection and Repair
Electro-Leak Location (ELL): Detect pinholes or weak seams using electrical methods.
Patching: Repair defects with 150mm x 150mm patches of the same material.
6. Cost-Benefit Analysis
While 2mm LLDPE liners have a higher upfront cost compared to thinner alternatives (e.g., 1mm HDPE), their longevity and lower maintenance requirements often result in a lower lifecycle cost. For example:
A 2mm LLDPE liner in a landfill application may last 100+ years, whereas a thinner liner could require replacement within 30–50 years.
Reduced seepage rates (e.g., <0.1 L/m²/day) minimize water treatment costs in potable water reservoirs.
7. Sustainability Considerations
LLDPE geomembranes contribute to sustainability by:
Preventing Groundwater Contamination: Protecting ecosystems from hazardous leaks.
Extending Asset Life: Reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Recyclability: Post-industrial scrap can be repurposed into new geomembranes or plastic products.
Conclusion
The 2mm LLDPE geomembrane liner represents a benchmark in containment technology, offering a robust blend of physical, mechanical, and chemical properties. Its versatility across industries, coupled with ease of installation and maintenance, makes it a preferred choice for engineers and project managers worldwide. By prioritizing quality control during manufacturing and adherence to best practices in the field, stakeholders can maximize the lifespan and efficiency of these liners, ensuring environmental and economic benefits for generations to come.