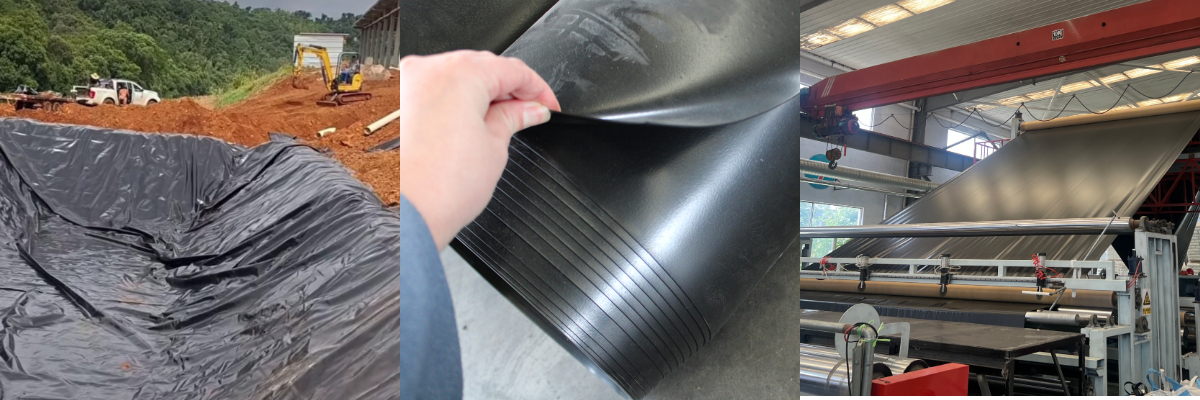
Waterproof 1mm HDPE Geomembrane
Exceptional Puncture and Tear Resistance: Withstands abrasive materials and heavy equipment during installation.
Thermal Stability: Maintains integrity in extreme cold (-50°C) or heat (100°C).
Low Lifecycle Costs: Reduces maintenance and replacement expenses over decades of use.
Waterproof 1mm HDPE Geomembrane: Engineering Resilience for Critical Containment Challenges
Introduction
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) geomembranes are pivotal in modern engineering for their impermeable, durable, and adaptable properties. The 1mm HDPE variant stands out as a heavy-duty solution for projects demanding robust containment, particularly in sectors like waste management, energy, and environmental protection. This article explores the technical innovations, environmental resilience, and practical applications of this material, supported by empirical data and case studies.
Technical Specifications: Precision and Power
The 1mm HDPE geomembrane is engineered to deliver unmatched performance in high-stress environments. Its thickness and molecular structure provide enhanced protection against physical and chemical degradation.
Table 1: Core Physical and Mechanical Properties
| Property | Specification | Test Method |
Thickness | 1.0 mm ± 5% | ISO 4593 |
Density | 0.950–0.970 g/cm³ | ISO 1183 |
Tensile Strength (MD/TD) | ≥ 45 MPa | ISO 527-3 |
Elongation at Break | ≥ 500% | ISO 527-3 |
Puncture Resistance | ≥ 800 N | ISO 12236 |
UV Resistance | > 3000 hours | ISO 4892-2 |
Thermal Stability | -50°C to 100°C | ISO 306 |
Compared to thinner membranes, the 1mm variant exhibits superior puncture resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for projects exposed to extreme temperatures or sharp debris.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance
This geomembrane excels in hostile environments, resisting degradation from aggressive chemicals, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. Its stability in acidic, alkaline, and organic solvent-rich settings ensures long-term performance.
Table 2: Chemical Resistance Performance
| Chemical Type | Exposure Duration | Performance Impact |
40% Sulfuric Acid (pH 0.5) | 30 days | No surface erosion |
25% Sodium Hydroxide | 30 days | Minimal swelling (<1.5%) |
Crude Oil | 7 days | No blistering or softening |
Methanol-Water Mixture | 14 days | No discoloration or cracking |
This resilience positions the material as a top choice for oil and gas containment, chemical processing, and hazardous waste landfills.
Diverse Applications in Modern Engineering
The 1mm HDPE geomembrane serves critical roles across industries:
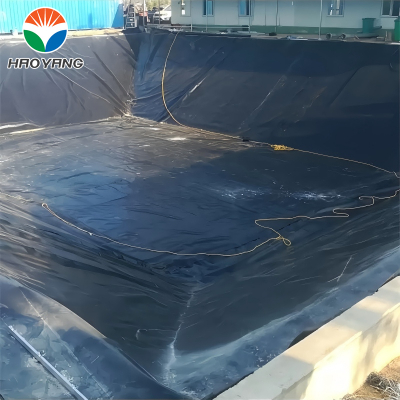
Municipal Solid Waste Landfills: Acts as a primary liner to prevent leachate migration.
Oil and Gas Reservoirs: Contains produced water and drilling mud.
Hydraulic Structures: Waterproofs dams, canals, and reservoirs in arid regions.
Agricultural Waste Lagoons: Seals manure and fertilizer runoff ponds.
A case study in North America demonstrated its use in a municipal landfill, where it reduced leachate seepage by 99% over a decade. In the Middle East, a desalination plant utilized the material to line brine evaporation ponds, maintaining integrity despite saline concentrations exceeding 15%.
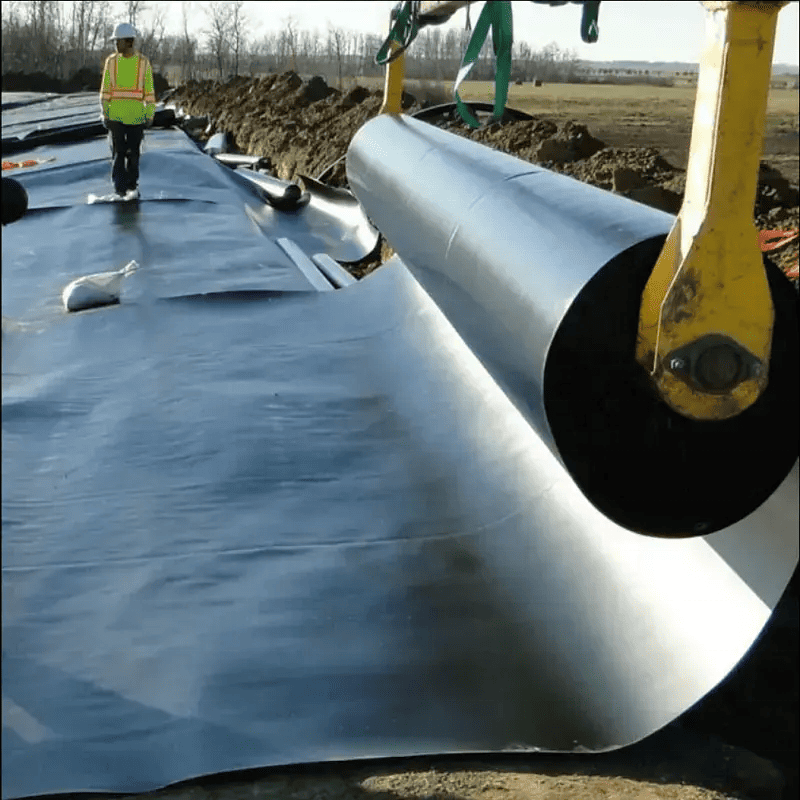
Installation and Long-Term Maintenance
Proper installation ensures optimal performance:
Substrate Preparation: Excavate sharp rocks, apply geotextile cushions, and compact substrates.
Seaming Techniques: Use extrusion welding for thick membranes to ensure airtight joints.
Quality Control: Conduct spark tests and pressure decay tests to detect leaks.
Routine inspections every 12 months are recommended, with repairs using HDPE-compatible patches.
Advantages of 1mm HDPE Geomembrane
Unmatched Durability: Withstands heavy loads, sharp objects, and temperature extremes, minimizing repair needs.
Broad Chemical Compatibility: Resists aggressive industrial and petrochemical substances.
Decades-Long Service Life: Maintains performance in permanent installations, reducing lifecycle costs.
Conclusion
The 1mm HDPE geomembrane represents the pinnacle of containment technology, offering unparalleled protection in the most demanding environments. Its combination of mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and adaptability makes it indispensable for infrastructure projects prioritizing safety and longevity. As global regulations on environmental protection tighten, this material will continue to be a cornerstone of sustainable engineering.