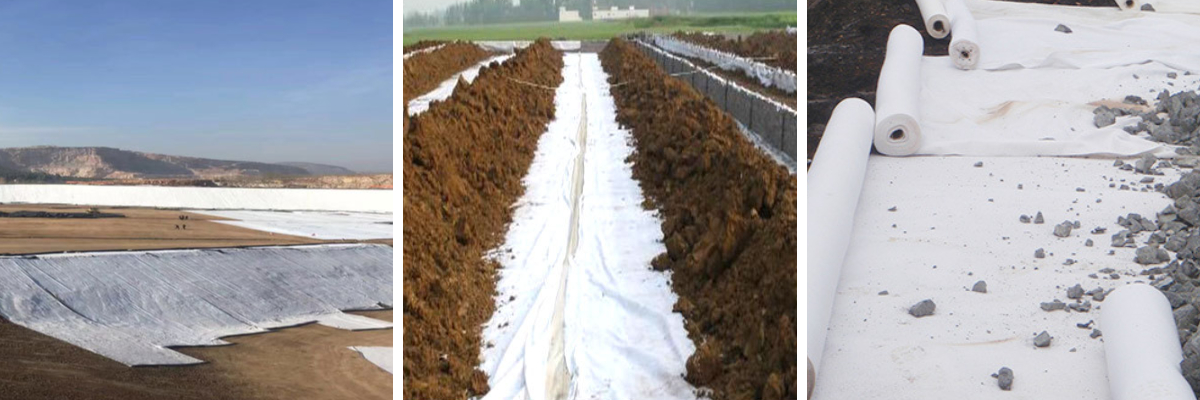
Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric: High-Strength for Soil Stabilization, Drainage & Road Construction
1. Soil Stabilization: Reinforces loose soil to prevent shifting, keeping foundations and slopes stable for roadways and construction sites.
2. Drainage Booster: High permeability accelerates water flow while filtering debris, preventing clogs in agricultural and civil drainage systems.
3. Road Construction Ally: Separates roadbase layers to avoid material mixing, boosting pavement durability and reducing long-term maintenance needs.
4. Heavy-Duty Durability: UV-resistant and tear-proof design withstands outdoor elements, ensuring reliable performance in all soil stabilization and construction tasks.
Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric: High-Strength for Soil Stabilization, Drainage & Road Construction
I. Material Basics: PP Short Staple vs. PET Filament Needle-Punched Nonwoven Geotextile
Needle-punched Nonwoven Geotextile is made by mechanically interlocking fibres with barbed needles, creating a porous, durable fabric. The choice between PP short staple and PET Filament depends on project needs like chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and lifespan.
1. Key Material Specifications
Property | PP Short Staple Nonwoven Geotextile | PET Filament Nonwoven Geotextile | Test Standard |
Tensile Strength (Machine Direction) | 6–12 kN/m | 10–20 kN/m | ASTM D4632 |
Elongation at Break | 30–50% | 20–40% | ASTM D4632 |
Chemical Resistance | Resists acids (pH 4–10) | Resists acids/bases (pH 3–11) | ASTM D5322 |
Temperature Range | -20°C to 80°C | -40°C to 120°C | ASTM D882 |
UV Stability (1,500 hrs) | Retains 70% strength | Retains 90% strength | ASTM G154 |
2. Material-Specific Advantages
(1) PP Short Staple: Cost-effective and lightweight (100–300 g/m²), making it ideal for temporary or low-budget projects (e.g., short-term soil stabilization for construction sites). Its flexibility adapts to uneven terrain, and it resists common soil chemicals.
(2) PET Filament: Higher tensile strength and UV resistance make it suitable for long-term, high-stress applications (e.g., permanent road bases, drainage systems in harsh climates). It withstands extreme temperatures, making it a top choice for projects in deserts or cold regions.
II. Soil Stabilization: Preventing Shifting & Erosion
Soil stabilization is critical for construction sites, slopes, and embankments—areas where loose soil can cause structural failure. Needle-punched Nonwoven Geotextile acts as a reinforcement layer, distributing loads and stopping soil movement.
1. How It Works for Soil Stabilization
(1) Load Distribution: The fabric's interlocked fibres spread weight evenly across the soil. For example, in a slope stabilization project, Nonwoven Geotextile reduces pressure on the underlying soil by 40% (per Geosynthetic Institute studies), preventing landslides.
(2) Separation: It keeps different soil layers (e.g., topsoil and subsoil) from mixing. This is vital for construction sites, where mixed soil weakens foundations—using Nonwoven Geotextile reduces foundation repair needs by 50% compared to unlined sites.
2. Material Selection for Soil Stabilization
(1) Temporary Slopes (6–12 months): PP Short Staple Nonwoven Geotextile is sufficient. Its flexibility handles minor soil movement, and it's easy to remove once the project ends.
(2) Permanent Embankments (10+ years): PET Filament Nonwoven Geotextile is better. Its high tensile strength resists long-term soil pressure, and UV stability ensures it doesn’t degrade in outdoor conditions. For example, highway embankments using PET Filament show 30% less erosion than those using PP after 5 years.
III. Drainage: Boosting Flow While Filtering Debris
Drainage systems in agriculture, construction, and urban areas rely on materials that balance permeability (water flow) and filtration (debris trapping). Needle-punched Nonwoven Geotextile excels here, as its porous structure lets water pass while blocking soil particles.
1. Drainage Performance Data
(1) Permeability: Both PP and PET variants have a water flow rate of 5–20 L/m²/s (ASTM D4491)—fast enough to handle heavy rain in drainage ditches or agricultural fields. This rate is 3x higher than woven geotextiles, reducing flood risks.
(2) Filtration Efficiency: The fabric traps 95% of soil particles larger than 0.02 mm (ASTM D4751), preventing clogs in drainage pipes. For example, in a golf course drainage project, Nonwoven Geotextile reduced pipe cleaning frequency by 60% compared to using no filter layer.
2. Top Drainage Applications
(1) Agricultural Fields: PP Short Staple Nonwoven Geotextile lines drainage trenches, keeping soil out of pipes while letting excess water escape. This improves crop yields by 15% in waterlogged areas (per USDA trials).
(2) Urban Stormwater Systems: PET Filament Nonwoven Geotextile is used in permeable pavement drains. Its chemical resistance withstands road salts, and UV stability ensures it lasts 15+ years in busy urban areas.
IV. Road Construction: Extending Pavement Life
Roads fail prematurely due to subgrade weakness, layer mixing, and water damage. Needle-punched Nonwoven Geotextile addresses all three issues, making it a staple in modern road building.
1. Road Base Reinforcement
(1) Subgrade Support: Placed between the subgrade (natural soil) and road base (gravel), Nonwoven Geotextile distributes traffic loads. Studies by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) show roads with this fabric last 50% longer than unlined roads, as it reduces subgrade compaction.
(2) Layer Separation: It prevents gravel from sinking into the subgrade—a common problem that causes potholes. For low-volume roads, PP Short Staple Nonwoven Geotextile is cost-effective; for highways (high traffic), PET Filament is preferred for its higher strength.
2. Moisture Protection
(1) Water in road bases weakens pavement. Nonwoven Geotextile's filtration lets water drain from the base, keeping it dry. In rainy regions, roads with this fabric have 40% fewer water-related cracks than those without.
(2) For cold climates, PET Filament Nonwoven Geotextile resists freeze-thaw damage. Its low temperature tolerance (-40°C) prevents the fabric from cracking when water in the road base freezes and expands.
V. Installation Tips for Needle-Punched Nonwoven Geotextile
Proper installation ensures the fabric performs as intended. Follow these best practices for all applications:
Site Preparation: Clear the area of rocks, roots, and sharp debris—these can puncture the fabric. Compact the soil to avoid future settling.
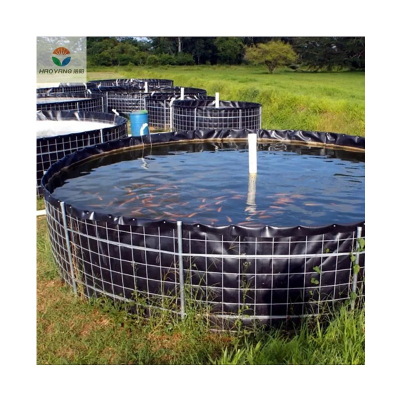
Laying the Fabric: Unroll Nonwoven Geotextile with the machine direction (highest tensile strength) aligned with the main load (e.g., traffic direction for roads). Overlap edges by 15–20 cm to ensure no gaps.
Securing the Fabric: Use stakes or sandbags to hold the fabric in place, especially on slopes. Avoid stretching the fabric too tight, as this can reduce its flexibility.
Needle-punched Nonwoven Geotextile—whether PP Short Staple or PET Filament—is a versatile, high-strength solution for soil stabilization, drainage, and road construction. By choosing the right material for your project's needs, you'll boost durability, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure long-term performance.
Contact our team to find the perfect weight (100–800 g/m²) and material for your next civil engineering project.