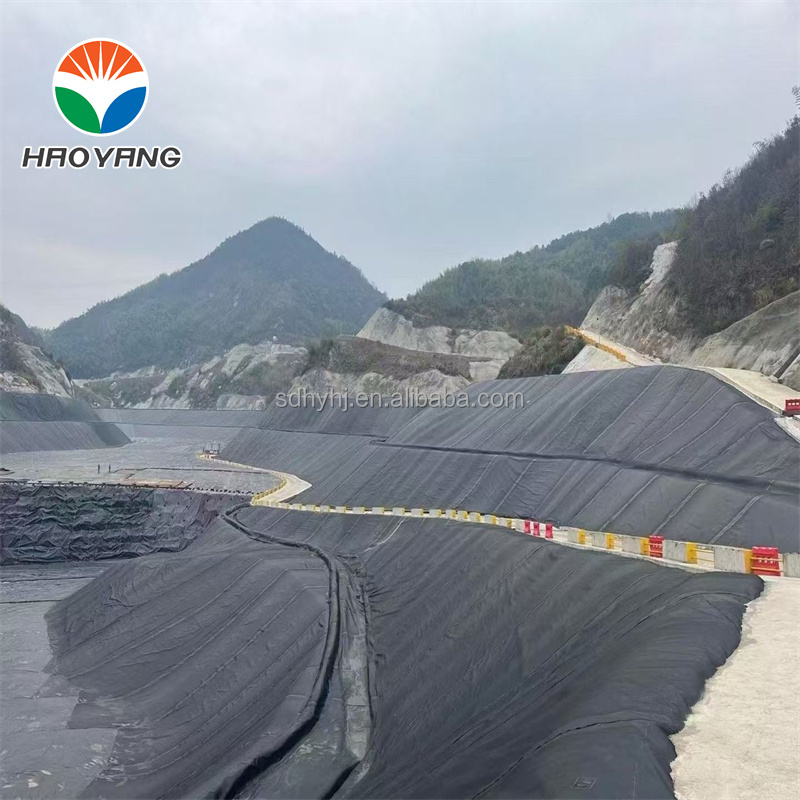
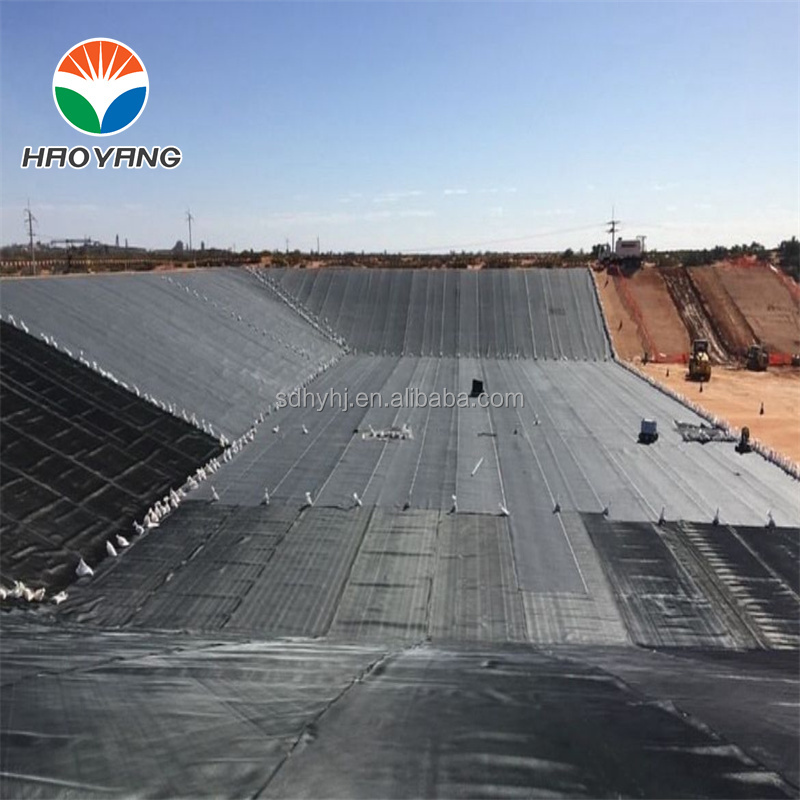
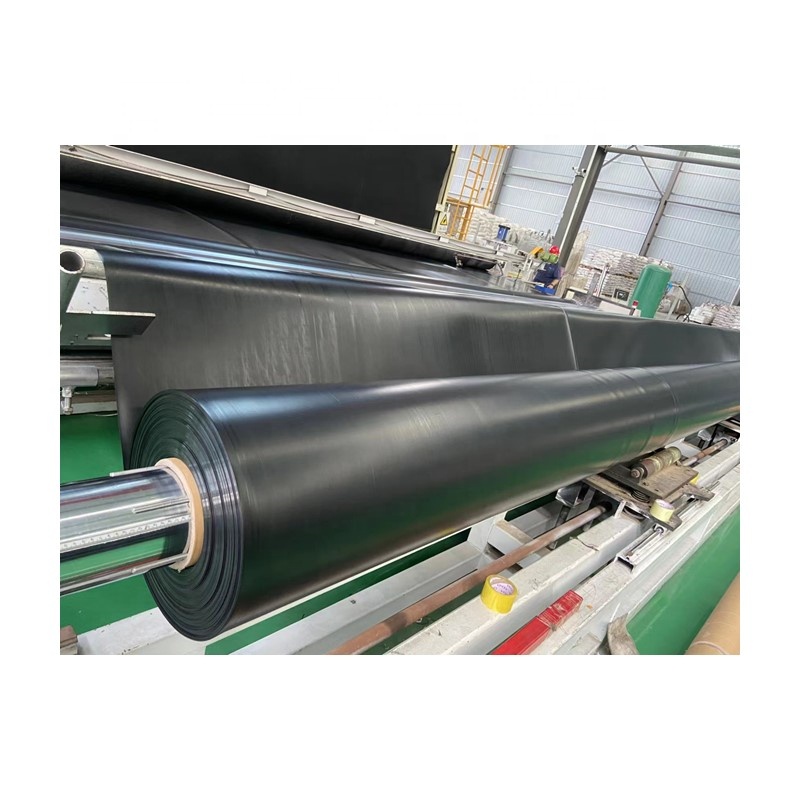
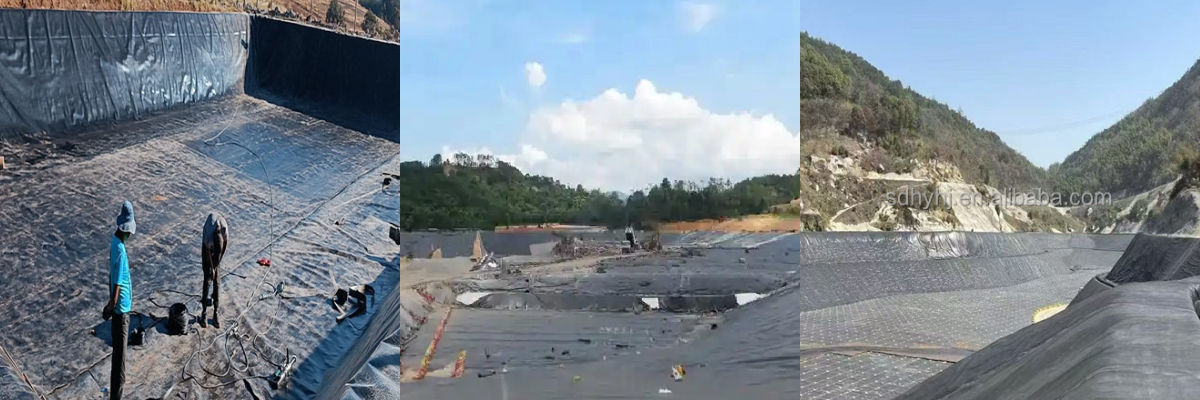
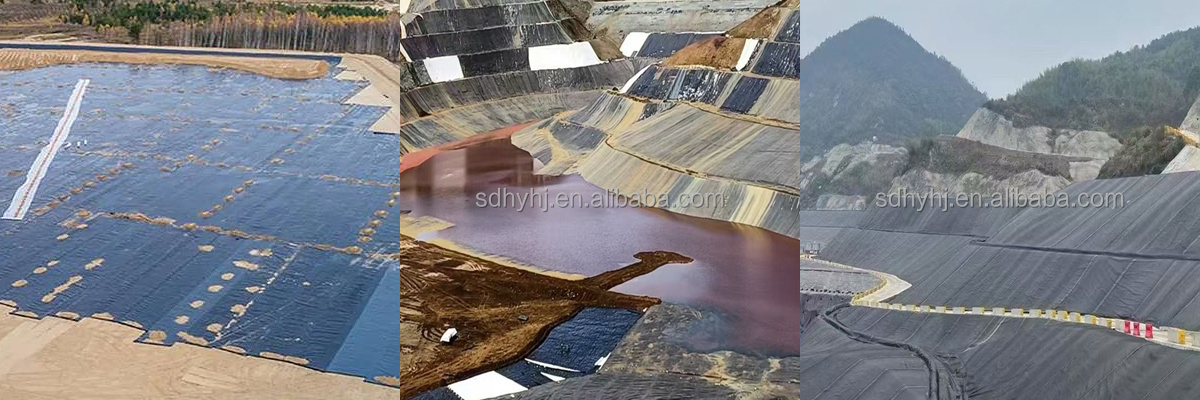
Geomembrane 1.5mm for Landfill
1.Superior Mechanical Durability: The 1.5 mm geomembrane exhibits a tensile yield strength of 22 N/mm and puncture resistance of 480 N, enabling it to withstand landfill stresses such as waste settlement, sharp objects, and construction equipment impacts.
2.Long-Term Environmental Stability: With UV resistance exceeding 500 hours and carbon black content optimized for anti-aging, the material retains integrity in exposed conditions for 50–70 years, minimizing replacement costs.
3.Cost-Effective Seepage Control: Compared to thicker alternatives (e.g., 2.0 mm), the 1.5 mm variant reduces material costs by 15–25% while meeting regulatory requirements for leachate containment, as demonstrated in projects like the Mexico City Landfill Expansion.
Geomembrane 1.5 mm for Landfill
Introduction
Landfills are critical infrastructure for solid waste management, but improper containment systems can lead to environmental contamination through leachate migration. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) geomembranes have emerged as the industry standard for landfill liners due to their impermeability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Among these, the 1.5 mm thickness variant strikes an optimal balance between mechanical strength and economic viability, making it widely adopted in global landfill projects. This article explores the technical specifications, performance advantages, and application scenarios of 1.5 mm HDPE geomembranes, supported by empirical data and industry insights.
Technical Specifications
Table 1: Core Physical Properties of 1.5 mm HDPE Geomembranes
| Parameter | Test Method | 1.5 mm Specifications | Industry Standards |
Thickness (mm) | ASTM D5199 | 1.50 ± 0.05 | 0.75–3.0 mm (ASTM/GRI GM13) |
Density (g/cm³) | ASTM D1505 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.935 (ISO 14216) |
Tensile Yield Strength (N/mm) | ASTM D6693 Type IV | ≥22 (LD/TD) | ≥18 (LD/TD) (GRI GM13) |
Tensile Breaking Strength (N/mm) | ASTM D6693 Type IV | ≥40 (LD/TD) | ≥33 (LD/TD) (GRI GM13) |
Elongation at Break (%) | ASTM D6693 Type IV | ≥700 | ≥600 (ISO 10319) |
Puncture Resistance (N) | ASTM D4833 | ≥480 | ≥360 (GRI GM13) |
Tear Resistance (N) | ASTM D1004 | ≥187 | ≥156 (GRI GM13) |
Carbon Black Content (%) | ASTM D1603 | 2.0–3.0 | 2.0–3.0 (ISO 11908) |
UV Resistance (hrs) | ASTM D5397 | ≥500 | ≥300 (ISO 4892-3) |
Table 2: Performance Comparison Across Thickness Variants
| Thickness (mm) | Yield Strength (N/mm) | Puncture Resistance (N) | Service Life (Years) | Cost/m² (USD) |
0.75 | 15 | 320 | 30–40 | 0.28–0.35 |
1.0 | 18 | 400 | 40–50 | 0.40–0.50 |
1.5 | 22 | 480 | 50–70 | 0.50–0.65 |
2.0 | 29 | 640 | 70+ | 0.75–0.90 |
Application Scenarios
Primary Liner Systems: Installed beneath waste cells to prevent leachate infiltration into soil and groundwater, complying with EPA Subtitle D standards.
Secondary Containment: Used as floating covers or secondary liners to enhance redundancy in critical landfills.
Closure Caps: Applied during landfill closure to limit gas emissions and surface water infiltration, as seen in the Shandong Province Landfill Rehabilitation Project.
Conclusion
The 1.5 mm HDPE geomembrane represents a technologically advanced and economically viable solution for modern landfill containment. Its balanced mechanical properties, longevity, and adaptability to diverse environmental conditions make it indispensable for sustainable waste management infrastructure. As global landfill standards evolve, this thickness variant is poised to remain a cornerstone of geosynthetic engineering.