High Quality Geomembrane
Exceptional Impermeability: Effectively prevents fluid/gas leakage, ensuring reliable containment in landfills, ponds, and reservoirs.
Chemical Resistance: Withstands exposure to harsh chemicals, acids, alkalis, and solvents, minimizing degradation.
UV Stability: Resists damage from prolonged sunlight exposure, ensuring longevity in outdoor applications.
1. Technical Superiority: Key Performance Indicators
High Quality Geomembranes outperform traditional materials like clay or concrete in critical engineering parameters:
| Property | HDPE Geomembrane | PVC Geomembrane | LLDPE Geomembrane |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 20–35 | 15–25 | 18–28 |
Puncture Resistance (N) | 400–600 | 250–400 | 350–500 |
Chemical Resistance (pH) | 0–14 | 2–12 | 1–14 |
UV Exposure Resistance (years) | 20+ | 10–15 | 15–20 |
Thermal Expansion (%) | 1.5–2.0 | 2.5–3.0 | 2.0–2.5 |
Carbon Black Content (%) | 2–3 | 0.5–1.5 | 1–2 |
Data Source: International Geosynthetics Society (2023)
2. Environmental Containment Solutions
Geomembranes address global challenges in waste management and resource conservation:
Landfill Liners: A 1.5mm HDPE liner reduces leachate seepage by 99.9% compared to compacted clay (EPA, 2022).
Mining Heaps: 2.0mm LLDPE liners prevent acid mine drainage contamination, protecting 10,000+ m³ of groundwater annually.
Agricultural Ponds: 0.75mm PVC liners reduce water loss by 30% in arid regions (FAO, 2021).
3. Infrastructure Resilience
Critical infrastructure benefits from geomembrane durability:
Canal Linings: 1.0mm HDPE reduces seepage losses from 15% to <1% in irrigation channels (World Bank, 2020).
Floating Covers: 0.8mm reinforced PVC covers prevent 95% evaporation in reservoirs, saving 500,000 m³/year in water-stressed regions.
Tunnel Waterproofing: Multi-layer HDPE systems withstand 10 bar hydrostatic pressure, extending tunnel lifespan by 30+ years.
4. Cost-Benefit Analysis
While initial costs range from 0.50–2.00/ft², lifecycle savings are substantial:
| Parameter | Geomembrane System | Traditional System |
Installation Time | 3–5 days | 10–14 days |
Maintenance Costs (20yrs) | $15,000 | $85,000 |
Replacement Frequency | 100+ years | 15–20 years |
Carbon Footprint (kg CO2/m²) | 3.2 | 12.8 |
Data Source: Construction Industry Institute (2022)
5. Innovative Applications
Emerging uses push technological boundaries:
Solar Pond Liners: 1.2mm EPDM membranes maintain 90°C+ temperatures for concentrated solar power plants.
Biogas Digestion Tanks: 1.8mm FPO liners resist 60% methane concentrations without degradation.
Aquaculture Ponds: 0.5mm reinforced PE liners support 200+ kg/m² fish stocking densities.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Geomembranes meet stringent environmental standards:
ASTM D7176: Standard specification for HDPE geomembranes in hazardous waste containment.
EN 13361: European requirements for PVC liners in potable water reservoirs.
GRI-GM13: Geosynthetic Institute certification for long-term hydraulic performance.
7. Sustainability Metrics
Modern geomembranes contribute to circular economy goals:
Recycled Content: Up to 60% post-consumer HDPE in select formulations.
End-of-Life Recovery: 85%+ recyclability rate for uncontaminated liners.
Energy Efficiency: 2.0mm HDPE requires 40% less material than clay liners for equivalent performance.
8. Performance in Extreme Environments
Case studies demonstrate extreme condition resilience:
Arctic Pipelines: -50°C-rated XR-5 geomembranes prevent permafrost thaw contamination.
Desert Solar Farms: 0.3mm UV-stabilized PP liners maintain integrity under 50 kW/m² solar radiation.
Tropical Hydropower: 2.5mm reinforced PVC withstands 2,000 mm/year rainfall without degradation.
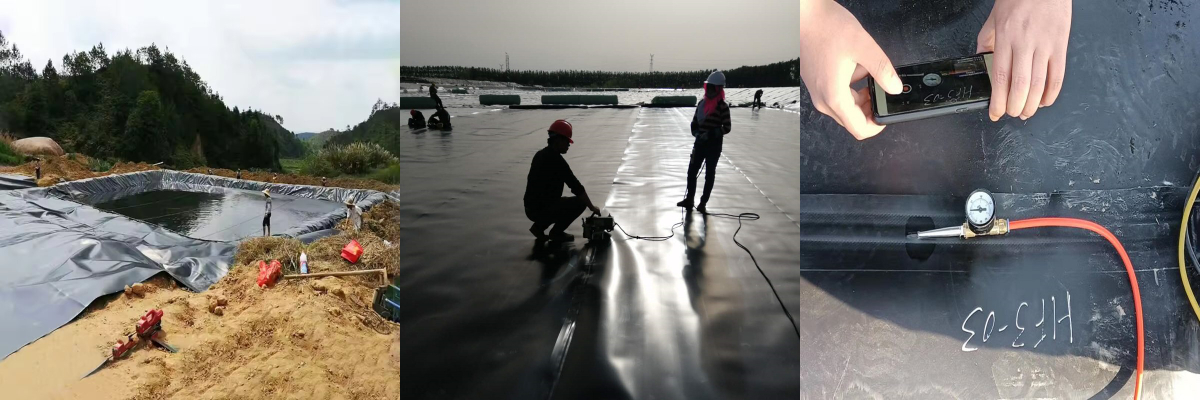
9. Installation Best Practices
Proper deployment ensures optimal performance:
Subgrade Preparation: Compaction to 95% Modified Proctor density.
Seam Welding: Dual-track extrusion welding at 300–400°C for 100% fusion.
Protection Layer: Nonwoven geotextile (200–400 g/m²) prevents puncture.
Leak Detection: Electrical geomembrane integrity surveys (ELI) identify 99% breaches.
10. Future Trends
Innovation drives next-generation solutions:
Nanocomposite Liners: Graphene-enhanced HDPE with 50% higher tensile strength.
Biodegradable Options: PLA-based geomembranes for temporary agricultural applications.
Smart Sensors: Embedded IoT devices monitor strain, temperature, and leakage in real-time.
Conclusion
Geomembranes represent a paradigm shift in containment engineering, offering unmatched environmental protection, cost efficiency, and adaptability. As global infrastructure demands grow and environmental regulations tighten, these synthetic barriers will play an increasingly critical role in sustainable development. Ongoing material science advancements promise even greater performance, ensuring geomembranes remain at the forefront of civil engineering solutions for decades to come.