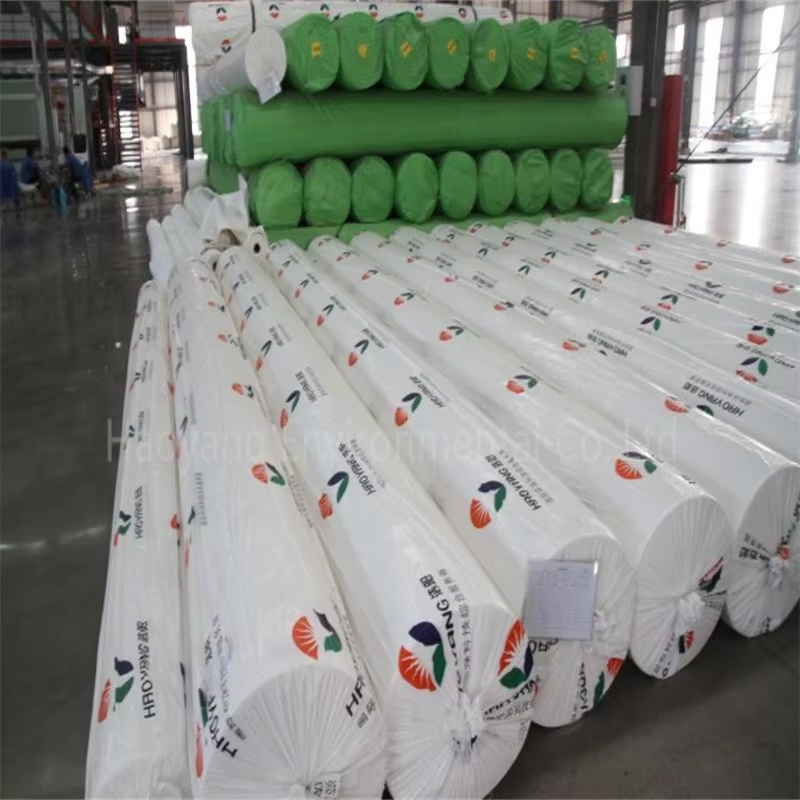
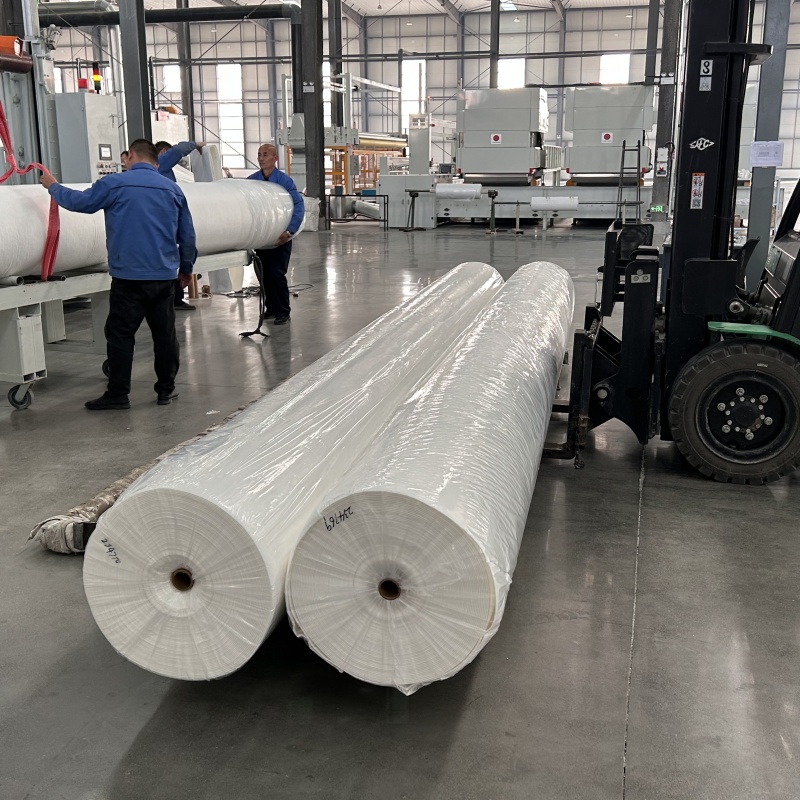
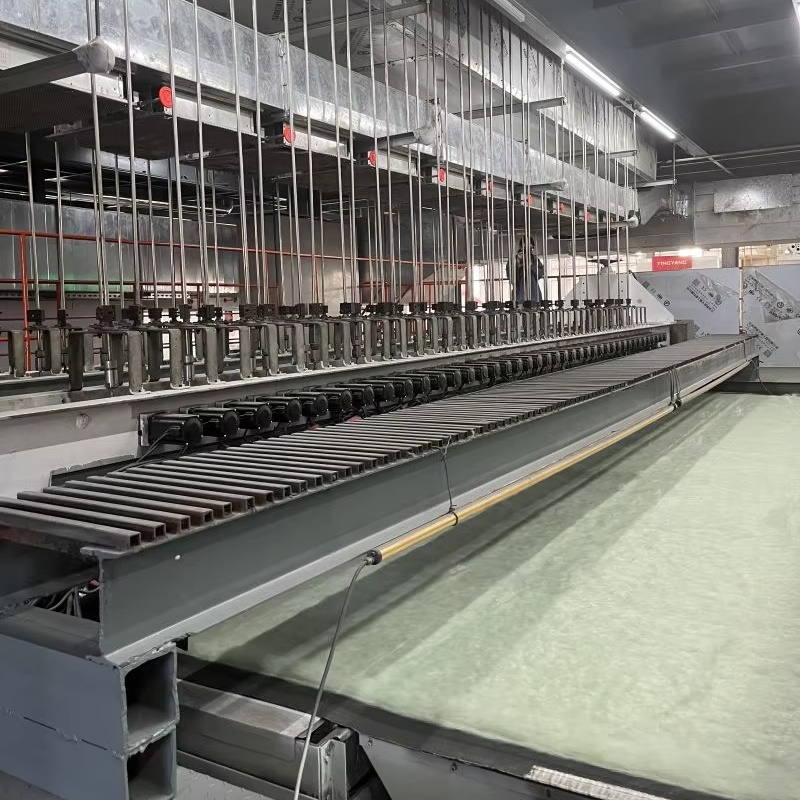
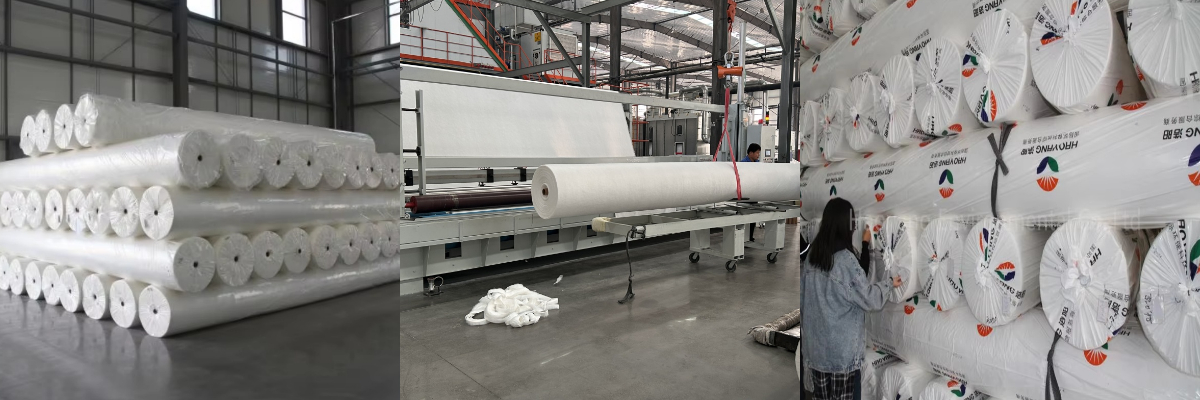
200g High-Strength Long Filament Geotextile
1. 200g high-strength long filament geotextile, with excellent tensile and tear resistance, capable of filtering water and preventing corrosion.
2. The geotextile weighs 200g and is made of long filament material, which has good toughness and can isolate soil layers.
3. 200g high-strength long filament geotextile, with strong resistance to penetration and puncture.
4. 200g geotextile made by long filament weaving, soft and closely adhering to the soil.
Geotextile introduction.
The 200g high-strength geotextile is made from high-quality polymer long-fiber filaments as the core material. The weight is precisely controlled at 200g/㎡. Through precise weaving technology, the fibers are evenly arranged and have strong continuity, forming a tightly structured and flexible fabric surface with no obvious seams. It can closely adhere to the soil, laying a foundation for its excellent physical properties and practical functions
Geotextile parameters
Category | Key Details (English) |
Material | Synthetic (PET/PP/PE, main); Natural (jute/cotton, rare) |
Structure | Woven (high strength); Non-woven (good filtration); Composite (balanced) |
Tech Params | Weight:100–800g/m²; Thickness:0.2–5.0mm; Permeability:10⁻³–10⁻¹cm/s |
Raw Materials | Synthetic: PET chips/PP granules; Natural: Raw jute/cotton (treated) |
Physical Prop. | Tensile strength:5–50kN/m; Tear resistance:0.5–15kN; Elongation:10–50% |
Chemical Prop. | Acid/alkali resistant; UV-resistant (with stabilizers); Hydrophobic (PP/PE) |
Application of Geotextiles
1. Roadbed reinforcement: Used in the construction of highways and railways, laid between soil layers to enhance the overall tensile strength of the roadbed, reduce soil settlement and deformation, and filter groundwater to prevent impurities from blocking, ensuring the long-term stability of the roadbed and extending the service life of the road.
2. Slope protection: Placed on mountain slopes and riverbanks, it can resist soil erosion caused by rainwater, by fitting with the terrain of the slope, avoiding soil collapse. It can also assist in planting vegetation to form an ecological protection system.
3. Hydraulic engineering: Suitable for the construction of dams and channels, it can separate different soil layers to prevent mixing, drain excess water to reduce the water pressure of the dam body, and is resistant to acid and alkali corrosion, enabling long-term operation in water environments and improving the safety of hydraulic facilities.
4. Tunnel lining: As an auxiliary material for the inner walls of tunnels, adhering to the lining structure can filter infiltrating water, protect the lining layer, reduce the impact of water seepage on the interior of the tunnel, and enhance the bonding between the lining and the soil, improving the tunnel's risk resistance capability.
5. Landfill: Used below the landfill's anti-seepage layer, it can isolate landfill leachate from the soil, prevent harmful substances from polluting groundwater resources, and have both filtering and reinforcing functions, ensuring the safety of the surrounding ecological environment of the landfill.
Case Studies of Geotextile Application
1. Indonesian Highway Construction Project: In a highway construction project in Indonesia, 200g high-strength long-staple geotextile fabric was used. It was laid between different material layers and, with its high tensile strength, enhanced the shear strength of the subgrade soil, effectively reinforcing the roadbed. At the same time, as a quick-drainage layer, the geotextile maintained good permeability and isolation functions, preventing the roadbed from collapsing due to rain erosion and significantly extending the lifespan of the highway.
2. American Landfill Project: A large landfill in the United States used 200g high-strength long-staple geotextile fabric as the key material below the anti-seepage layer. It isolated the landfill leachate from the soil, prevented harmful substances from polluting groundwater, and its filtering function prevented impurities from blocking the drainage system, providing a strong guarantee for the safety of the surrounding ecological environment of the landfill site. The effect has been good over many years of use.
3. Dutch Coastal Protection Project: In coastal protection projects in the Netherlands, 200g high-strength long-staple geotextile fabric was used to resist seawater erosion and wave impact. With its corrosion resistance and high strength, it closely adhered to the coastal terrain, strengthened the coastal soil, reduced soil erosion, assisted in the root growth of vegetation, and constructed a stable ecological protection system, playing an important role in protecting the coastline.
The application method of geotextiles
1. Base surface treatment: Before construction, the base surface needs to be cleaned to remove debris such as gravel and weeds. The base surface should be leveled to avoid any protrusions or depressions. If the base surface is wet, proper drainage should be implemented to prevent damage to the geotextile fabric due to unevenness of the base surface or impairment of its functionality.
2. Cutting and laying: Precisely cut the geotextile fabric according to the project dimensions to avoid waste and excessive splicing. During laying, flatten and stretch the fabric to ensure it adheres to the base surface. The width of the adjacent edges' overlap should be controlled at 10 - 15 cm to maintain overall continuity.
3. Fixation operation: Use sandbags, U-shaped nails or stitching to fix the geotextile fabric. Especially at slopes and corners, more fixation points should be set to prevent displacement of the fabric surface due to wind or external forces, ensuring the stability of the laid fabric.
4. Layer coordination: If used in combination with other materials (such as anti-seepage membranes), the geotextile fabric should be evenly laid between the two materials to avoid sharp objects scratching other materials. At the same time, ensure that the geotextile fabric is closely adhered to other materials to achieve a synergistic effect.
5. Post-laying inspection: After laying, conduct a timely inspection to check for any damages, loose connections, etc. Damaged areas should be repaired with patches made of the same material of the geotextile fabric. Ensure that the overall function of the geotextile fabric is intact and meets the engineering requirements.
The 200g high-strength long filament geotextile produced by Haoyang Environment has remarkable advantages.
1. In terms of production process, it adopts advanced international technology and eighteen patented technologies including double screw extrusion, ensuring product quality. Its strength far exceeds that of its competitors. Under the same weight, its tensile strength in all directions is excellent, effectively resisting external forces and ensuring the stability of the project. The product has good corrosion resistance and anti-aging properties, and can maintain stable performance in harsh environments such as acid and alkali and long-term outdoor conditions.
2. It is also excellent in permeability and drainage performance. The thick needle-punched forming structure ensures good planar drainage and vertical permeability, and its performance remains stable even after many years, providing reliable support for various engineering drainage, filtration and other needs.